2020 has been a terrific year in terms of scientific discoveries. Even though numerous catastrophes have occurred as a result of the emergence of the novel coronavirus right from the start of 2020, scientific feats achieved in this year are matchless compared to past years.
Let us look at the world’s best 10 scientific breakthroughs of the year 2020.
1. The Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) & COVID-19 Research
The greatest of all scientific discoveries was the viral genome decoding and vaccine development for the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). With the alarming transmission rates and death tolls from COVID-19, researchers and medical care workers have functioned promptly as well as exceptionally towards resolving this worldwide conundrum.
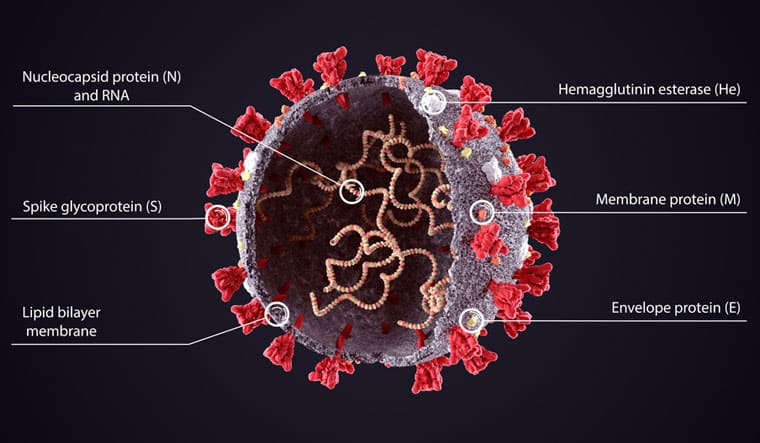
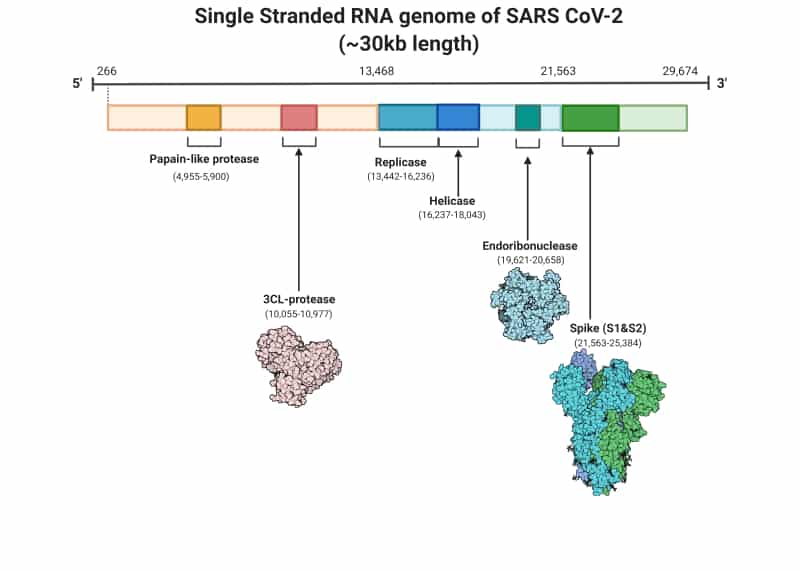
COVID-19 research triumphs in the past year range from fundamental characterization of the virus & disease to potential therapeutic measures to treat and curb the infections. Complete genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 was first achieved by the Wuhan Institute of Virology and was shared on GISAID by January 2020. Further disease conditions were categorized into mild, moderate, severe, or asymptomatic COVID-19. Later, the routes of transmission, the infecting parts of COVID-19 were found in the same year.
The lightning
speed invention of the COVID-19 vaccine was another scientific breakthrough in 2020. Merely after a year, the first vaccine for COVID-19 by Pfizer-BioNTech was developed, manufactured, approved, and is being distributed. Several other distinct vaccine candidates are also on the verge of distribution. Drugs targeting coronavirus was discovered. This all happened in a short span of a year, which previously took many years to complete. Hats off to the scientists and people behind these wondrous discoveries. Without them, 2020 wouldn’t be this victorious in the science realm.2. CRISPR-Cas9 Technology Into Human Life
The most refined genetic engineering technology, the CRISPR-Cas 9 was recognized for Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020. The diversity and convenience of this technique facilitated the genetic modification of organisms that was impossible to do before with conventional genetic engineering tools. In 2020, CRISPR-Cas9 technology was first applied in humans for modifying the gene causing blindness.
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2020 Goes To CRISPR Gene Editing
3. Immunotherapy for Human Brain Cancer: Canine Bone Cancer Treatment to Human Trials
The successful treatment of bone cancer in dogs using immunotherapy mediated researchers to conduct study trials in human brain cancer. This is one of the top 10 scientific breakthroughs in 2020. Scientists from the College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Missouri effectively treated osteosarcoma in 14 dogs, which is a common cancer condition seen in dogs, employing immunotherapy techniques. Researchers partnered with the biotech firm ELIAS Animal Health to carry out the study.
The dog’s immune response was boosted with their own white blood cells retrieved and grown in the lab. Since humans and dogs share a similar immune system, a parallel therapeutic approach can be applied to human cancers, according to the researchers. This study was able to convince the FDA to permit trials in humans with a pathological condition called glioblastoma multiforme, which is an aggressive, rare, and difficult to cure brain cancer type.
4. Development of Plastic Consuming Super Enzymes
Plastic has been a persisting issue in pollution all over the world. People nowadays are known to involuntarily breathe and consume microplastics. To reduce the plastic waste in the surroundings and limit the excessive usage of fossil fuels, a super enzyme was engineered by binding two distinct enzymes from a plastic consuming bacteria.

A recent study in 2020 gave insights on plastic devouring bacteria and their super enzyme to break down this persisting polymer into monomeric form, which can be further used to make plastic, rather than relying on fossil fuel. These isolated super enzymes act on a widely used plastic for the production of clothing, carpets and one-time-use bottles termed PET (Polyethylene terephthalate).
5. Protein predictors
Scientists have been struggling to detect the key principles that elucidate the conformation of proteins when they fold. There is a myriad of ways in which a protein can fold depending on the bonds of its unit component, the amino acid. Drug designing or a clear understanding of the working of a protein or what happens in a disease-all require the protein’s 3-D structure concept.
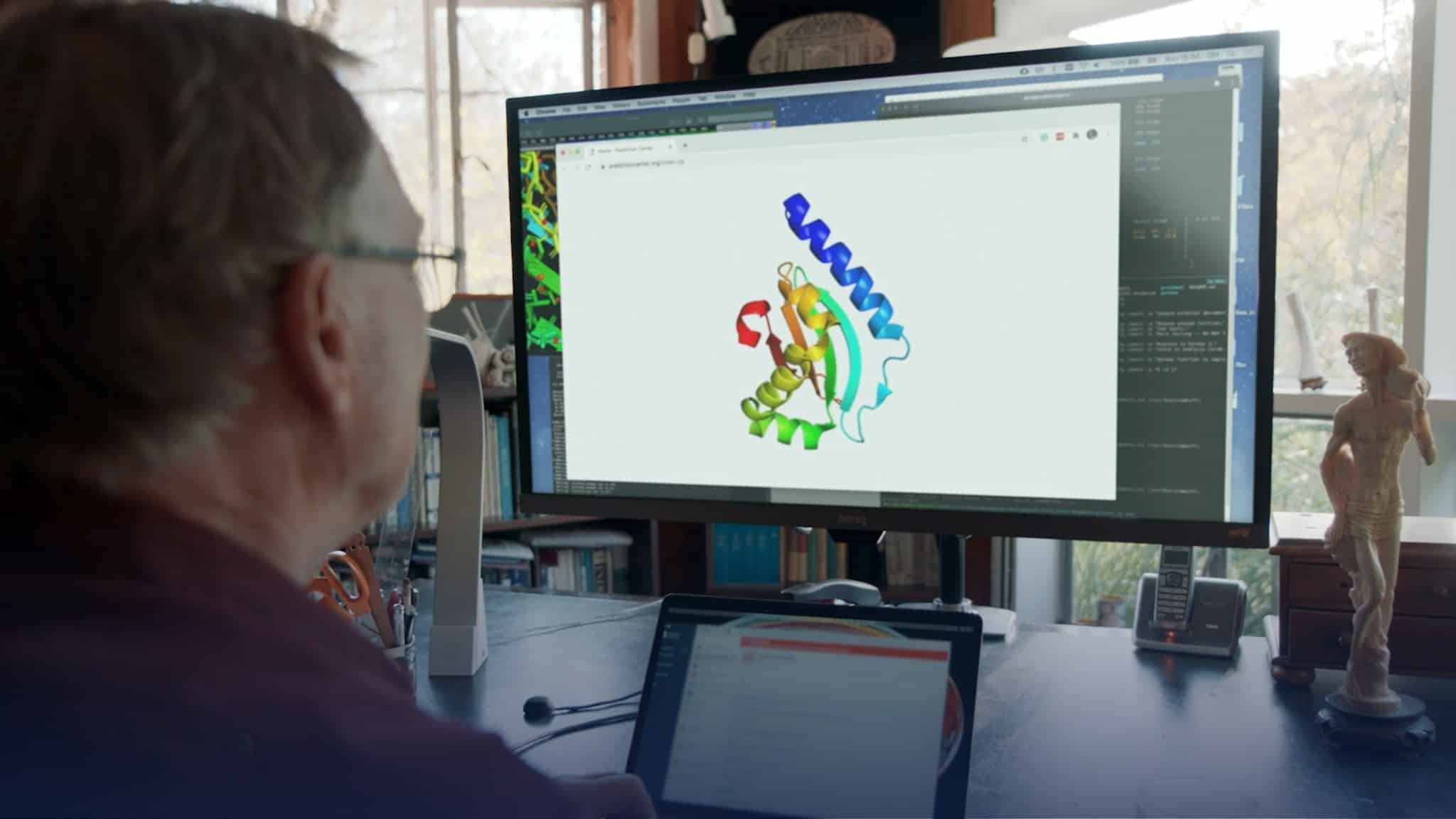

A successful protein prediction can enable potential new medicine development with the specified interested structure. It paves way for many medical applications ranging from new cancer therapeutics to possible antidepressants.
In 2020, Deepmind’s AI technology called AlphaFold has become a boon to this 50- year old concern. Using this technology, researchers from the biomedical sector can rapidly check the available drugs to see the effective drug against the disease and tailor the drug design accordingly.
6. Lab-grown meat
Feeding the ever-growing population is a constantly bothering issue. Scientists worldwide have been trying to create cultured or lab-grown meat as a substitute for farm-grown meat. A US firm Eat Just was able to make lab-grown meat which was included in an eatery in Singapore in 2020. The cultured meat tasted similar to the conventionally grown meat, according to the reports.
As meat demands are rising all over the world, this technology has the potential to resolve the problem. This can be a way to stop the dependence on barbaric farming methods and forming a food system that satisfies the world’s requirements for meat products ethically.
7. Prospective method to put an end to dengue fever
Dengue is the most prevalent arthropod-borne viral disease of humans, causing a considerable burden in the tropics. Both vaccines and conventional methods to reduce infections are not effective. The introduction of the bacterial strains of Wolbachia in Aedes aegypti has significantly reduced the virus multiplication in the carrier mosquito.
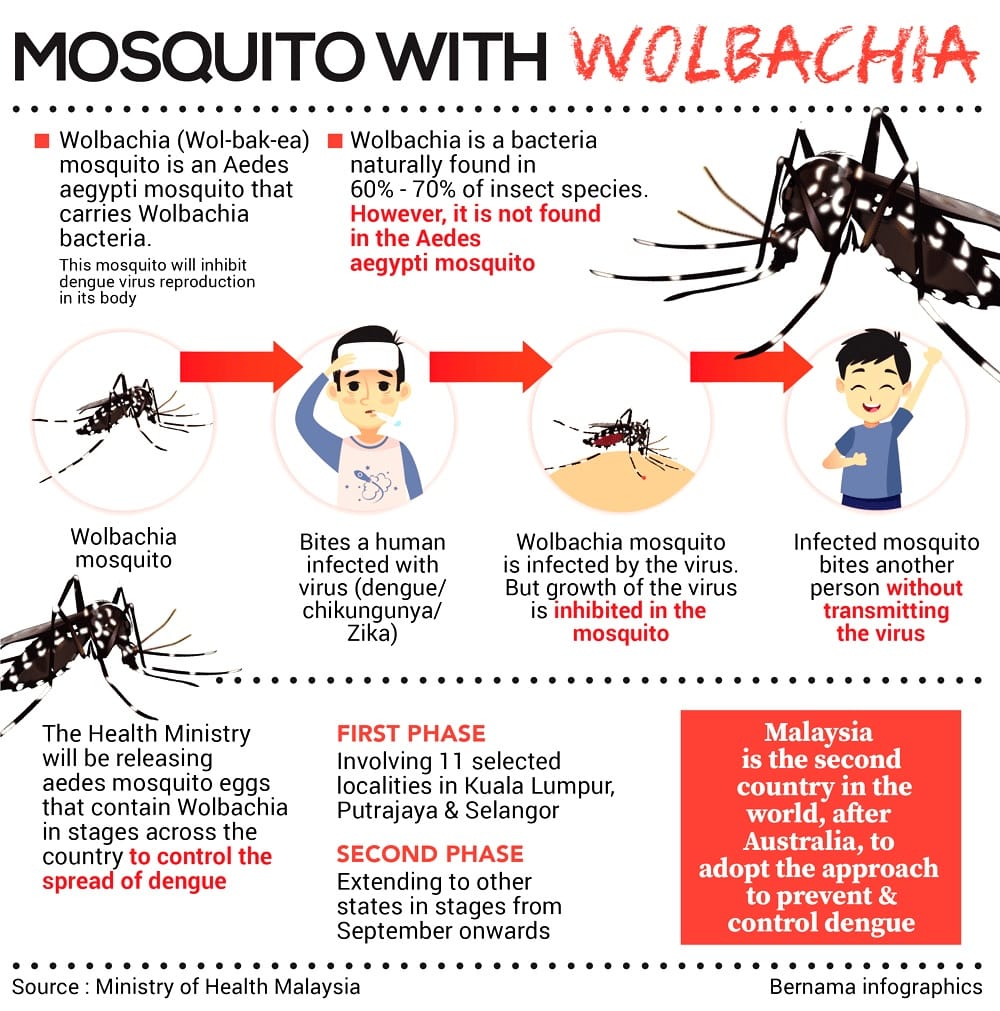
Adi Utarini and her team successfully reduced dengue incidents by 77% in different regions of Indonesia. They have accomplished this task by setting off mosquitoes with Wolbachia bacterial strains which can effectively cease them from spreading the viral infection. This study was the first & novel randomized controlled trial, a benchmark approach in clinical research studies, for curbing dengue.
8. A new organ found in Human Anatomy
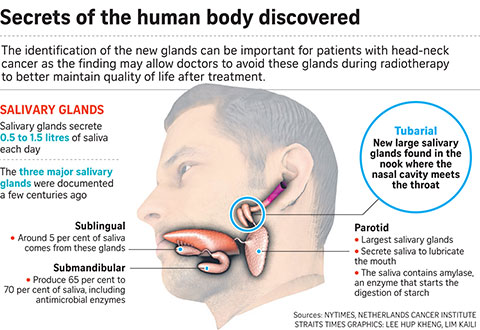
Dutch scientists fortuitously discovered a new tiny organ in the human body. While studying tumor-like growths using PSMA PET/CET, they accidentally found the so-called tubarial glands that are positioned in the upper region of the throat, another top 10 scientific breakthroughs in 2020. The main project supervisors believe that the small, new-fangled tubarial glands are to lubricate and moisten the oropharynx and nasopharynx regions.
9. Cryo-electron microscopy attains an atomic resolution
In structural biology, if scientists can directly visualize macromolecules like proteins clearly, it enables them to easily discern how the protein’s 3-D conformations can affect biological functions.
cryo-EM or single-particle cryo-electron microscopy facilitated in providing sharpest images of the positions of each atom in a protein, by achieving atomic resolution. This could potentially be applied for COVID-19 drug discovery.
10. Construction of living robots
Researchers from the US have developed the first-ever self-healing and living bots in 2020. These xenobots were built by isolating live embryonic stem cells from frogs. It is termed after the African clawed frog, Xenopus laevis, from which stem cells were collected. Stem cells are pluripotent in nature, thus can form any cell type.
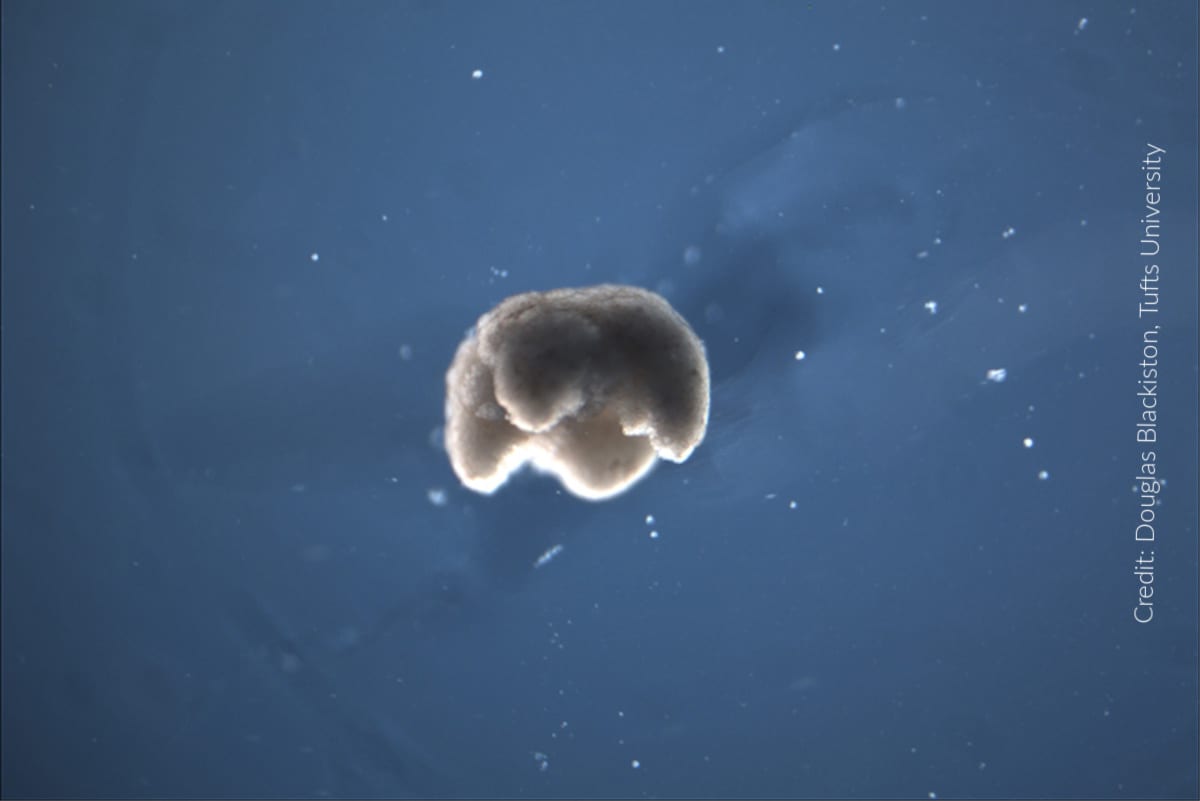
After isolating these pluripotent stem cells, it is incubated. The grown heart and skin cells were later amended and merged into body forms to walk, or even swim by supercomputers. These small living bots of millimeter size-able to move within the human body. These xenobots can survive for many days devoid of food and collectively work in groups. Xenobots also has self-healing capacity. This was found when scientists split a robot, it restored back and started moving.
Unlike the conventional robust, xenobots don’t possess a robotic arm or any shiny gears. Rather, these bots appear like a small glob of mobile pink flesh. Xenobots, in the near future, could be applied to get rid of radioactive litter, remove microplastics from the water bodies, deliver drug substances, or even remove plaque from our arteries. Besides these applications, xenobots could also be used to explore human longevity and health advancements.
Top 10 Scientific Breakthroughs in 2020

































Wow. Every discovery amazed me!
Great. Scientist update in 2020