An Overview of ELISA – Types of ELISA, ELISA Kits, ELISA Buffer-Probes
ELISA Which stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Otherwise called EIA -enzyme immunoassay) is a widely used immunoassay technique for detection & quantification of peptides, proteins, and antibodies. Along with western blotting, it is one if the most used technique with vast applications in the field of microbiology, owing to its rapid experimentation results unlike – radioimmunoassay.
Working Principle behind ELISA
96 Welled polystyrene plates are generally used in ELISA techniques. Each well is incubated with a different type of serum with the presence of positive & negative control serum in two wells. Further, an antigen or antibody must be immobilized on a solid surface. Antigens or antibodies present in the serum are then captured by a corresponding Antigens or antibodies on the solid plate. The plate is then washed to eliminate any unbound antibodies or antigens and is further subjected to a series of wash buffers.
A secondary antibody is then utilized For the detection of any bound antibodies or antigens. The secondary antibody is attached to an enzyme label such as peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase and is added to each well. Followed by an incubation period unbound secondary antibodies are washed off. Upon addition of a suitable substrate, the enzyme reacts to produce a color. This color is then used to measure the function or quantity of antigens or antibodies present in the given sample, with the major factor to be tested is the color density, which is measured at 450nm.
The intensity of the color gives an indication of the amount of antigen or antibody. The most crucial step of an ELISA is the detection stage with a highly specific antibody-antigen interaction. The choice of the substrate in ELISA depends upon the required assay sensitivity and also the type of instrumentation available for signal-detection.
Table: Common Enzyme Labels Used in ELISA For antibody conjugation
| Enzyme Label Name For Use In ELISA | Source | Reaction Catalyzed |
| Peroxidase | Horseradish | H2O2+ Oxidisable substrate —-> Oxidized Product + 2H2O |
| Alkaline Phosphate | Calf Intestine | R-O-PI + H2O —> R-OH + PI |
| Beta-Galactosidase | E.coil | Beta-D-Galactoside + H2O—->Galactose + Alcohol |
Table of Contents
VIEW ELISA KITS LIST
STEPS IN ELISA SIMPLIFIED
STEP 1: Antigen from a sample – immobilized on a surface – polystyrene microtiter plate – through charge interactions.
STEP 2: Specific antibody added – binds to an antigen
STEP 3: Antibody-linked to enzyme
STEP 4: Enzyme substrate added to complete the reaction
STEP 5: Detectable signal produced – color change detected.
STEP 6: Between each step – wash with a mild detergent solution – to remove extra antibodies
Types of ELISA / ELISA Formats
ELISAs can also be performed with modifications in the basic procedure, based on the experimentation requirement. Based on the key step of immobilization, ELISA can be performed in different ways which are mentioned below:
- Direct ELISA
- Indirect ELISA
- Sandwich ELISA
- Competitive ELISA
CHECK ELISA KIT PRICES
DIRECT ELISA STEPS
Best Suitable for: analyzing immune response to an antigen.
- A buffered solution of the antigen to be tested for is added to each well of a microtiter plate, where it is given time to adhere to the plastic through charge interactions.
- A solution of non-reacting protein, such as bovine serum albumin or casein, is added to well (usually 96-well plates) in order to cover any plastic surface in the well which remains uncoated by the antigen.
- The primary antibody with an attached (conjugated) enzyme is added, which binds specifically to the test antigen coating the well.
- A substrate for this enzyme is then added. Often, this substrate changes color upon reaction with the enzyme.
- The higher the concentration of the primary antibody present in the serum, the stronger the color change. Often, a spectrometer is used to give quantitative values for color strength.
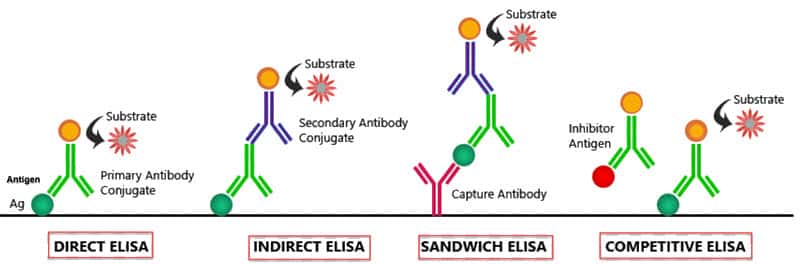
STEPS INVOLVED IN INDIRECT ELISA
Best Suitable for: determining total antibody concentration in samples.
- Primary unlabelled antigen – bound to the solid surface
- Antigen bound to this antibody
- Secondary antibody – labeled with an enzyme
- A substrate that interacts with an enzyme to give visual detectable signals
SANDWICH ELISA
Best Suitable for: analysis of complex samples as antigen purification not required prior to measurement.
This is considered to be as the most powerful ELISA format as it is highly sensitive & robust. In this, the analyte to be measured is “sandwiched” between two primary antibodies. Steps involved in SANDWICH ELISA are listed below:
- A surface is prepared to which a known quantity of capture antibody is bound.
- Any nonspecific binding sites on the surface are blocked.
- The antigen-containing sample is applied to the plate and captured by the antibody.
- The plate is washed to remove unbound antigen.
- A specific antibody is added and binds to the antigen (hence the ‘sandwich’: the Ag is stuck between two antibodies). This primary antibody could also be in the serum of a donor to be tested for reactivity towards the antigen.
- Enzyme-linked secondary antibodies are applied as detection antibodies that also bind specifically to the antibody’s Fc region (nonspecific).
- The plate is washed to remove the unbound antibody-enzyme conjugates.
- A chemical is added to be converted by the enzyme into a color or fluorescent or electrochemical signal.
- The absorbance or fluorescence or electrochemical signal (e.g., current) of the plate wells is measured to determine the presence and quantity of antigen.
BEST QUALITY ELISA KITS AT LOWEST PRICE
COMPETITIVE ELISA STEPS
Best Suitable: when only one antibody is available for the antigen of interest. It is also helpful in the detection of small antigens that cannot be bound by two different antibodies such as in the sandwich ELISA technique.
- Unlabeled antibody is incubated in the presence of its antigen (sample).
- These bound antibody/antigen complexes are then added to an antigen-coated well.
- The plate is washed, so unbound antibodies are removed. (The more antigen in the sample, the more Ag-Ab complexes are formed and so there are less unbound antibodies available to bind to the antigen in the well, hence “competition”.)
- The secondary antibody, specific to the primary antibody, is added. This second antibody is coupled to the enzyme.
- A substrate is added, and remaining enzymes elicit a chromogenic or fluorescent signal.
The reaction is stopped to prevent eventual saturation of the signal.
Table : Advantages & Disadvantages of Various Types of ELISA KITS
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| Direct Elisa |
Shorter protocol |
Higher background noise than indirect ELISA No signal amplification. Low flexibility: primary antibody must be conjugated. |
| Indirect ELISA | Signal amplification: numerous secondary antibodies will bind to the primary antibody. Economical – as less labeled antibodies are needed. High flexibility: the same secondary antibody may be reused for several primary antibodies. |
Longer protocol when compared to Direct ELISA Cross-reactivity can be seen from the secondary antibody. |
| Sandwich ELISA | Highly Sensitive in Comparison to all other types of ELISA High specificity: involves two antibodies detecting different epitopes on the same antigen. Suitable for complex samples. High flexibility |
Demanding protocol: finding two antibodies against the same target that recognize different epitopes and work well together can be challenging at times. |
| Competitive ELISA | crude or impure samples can be used.
Maximum flexibility in experimental setup since it can be based on direct, indirect or sandwich ELISA. |
Depends on base ELISA selected. |
APPLICATIONS OF ELISA
- Medical diagnosis
- Handy tests – positive & negative
- Genetic engineering
- Pathological diagnosis
- Hematological studies
- Food analysis
- Other research Purposes
Ready to use ELISA KITS
It is very important for one to buy the right type of ELISA Kit suitable for your experiment. There are many ready to use ELISA Kits commercially available by various manufacturers with different specifications, well number and packaging. Below mentioned are few tips you must go through before buying an ELISA Kit.
- Specificity
- Quantity of the Sample to be analyzed
- Quality of samples to be analyzed
- Type of Analyte to be detected
- Purpose of the analysis
- Detection system
- Budget
Best Quality ELISA Kits can be purchased online from Biotecnika Prime. We provide ELISA Kits manufactured from top companies at a very reasonable & affordable price. Just select the ELISA kit you are looking for @ Labs.biotecnika.org, look for the required specificity, host reactivity, Type of samples to be analyzed, Well size etc. Some of the most popular ELISA kits frequently bought from us are listed below:
- Human IRF3(InterferonRegulatoryFactor3) ELISA kit
- Mouse RAB35(Ras-relatedproteinRab-35) ELISA Kit
- Mouse FⅦ(CoagulationFactorⅦ) ELISA Kit
- Rat APLNR(ApelinReceptor) ELISA Kit
- P-human scfr-stem cell factor receptor elisa_kit
- Rabbit Preptin ELISA Kit
- Pg(Progesterone) ELISA Kit
- OT(Oxytocin) ELISA Kit
- Human Preptin ELISA Kit
- Mouse sCD146(Soluble Cluster of Differentiation 146) ELISA Kit
- Mouse TLR7(TollLikeReceptor7) ELISA Kit
- Human GLP1R(Glucagon-like Peptide1 receptor) ELISA Kit
- Mouse Ang1-7(Angiotensin1-7) ELISA Kit
- GSH(Glutathione) ELISA Kit
- HIS(Histamine) ELISA Kit
- DA(Dopamine) ELISA Kit
- BH4(Tetrahydrobiopterin) ELISA Kit
- Bb(Bilirubin) ELISA Kit
- ADT(Androsterone) ELISA Kit
- ACH(Acetylcholine) ELISA Kit
- Pregnenolone ELISA Kit
- Rat NEFH(Neurofilament, Heavy Polypeptide) ELISA Kit
- Cortisol ELISA Kit
ELISA PLATES & ELISA PROBES
Pre-coated ELISA plates are available to buy online. Various principal manufacturing companies sell optimized & ready to use ELISA kits with a 96-well strip plate pre-coated with an antibody specific to the antigen of interest. Most of the ELISA plate kits come in combination with recombinant protein standard, buffer & reagents for easy calorimetric detection.
A wide variety of conjugate & ELISA probes are available with vivid applications. These probes come handy in ELISA detection stage and may include secondary antibodies and conjugates, antibody-binding proteins and conjugates and others.
ELISA BUFFERS & SUBSTRATES
Biotecnika Prime has a vast range of ELISA Blocking Buffers & Substrates. All ELISA Buffers are manufactured with a high-performance washing solution for all types of ELISA formats. Usage of optimized high-quality pH stabilizers, slats & detergents shoots up the efficiency of the ELISA washing stage, hence reduced background noise & increased signal can be achieved.
Keywords: ELISA Kits, Types of ELISA, ELISA Type, Direct ELISA, INDIRECT Elisa, Competitive ELISA, Sandwich ELISA, Best ELISA, ELISA applications, ELISA Formats, ELISA Probes, ELISA antibodies, ELISA buffers, ELISA reagents, Best price for ELISA, ELISA price List, ELISA KIT Pricing, Buy ELISA online, ELISA Kit Buffer, ELISA Immunoassay, EIA technique, ELISA technique, ELISA method, Steps in ELISA, ELISA Kits List India, ELISA Kits Lits U.S, ELISA Kits List China, ELISA Kits List U.K, ELISA Kits Thermo Fisher, ELISA Kits Online, Kinds of ELISA, Purchase ELISA Kits, ELISA overview, Overview of ELISA, ELISA protocol, ELISA Procedure, ELISA kits buy in India, ELISA Kits 96 well, 96 Well ELISA Kits, ELISA plates, ELISA reagents, ELISA probes, ELISA conjugates.