Novel Sewage Treatment Plant By IISc and CST Scientists
India is ranked in the recent category of stressed nations in the world. Niti Aayog study conducted in 2018, reported that water availability per person will drop from 1544m³ in 2011 to 1465m³ in 2025. Rising water woes of the nation will eventually jeopardize the balance of living- poor hygiene practices, climate alterations, food security, and fights for water use. A possible way to mitigate this issue is by recycling and reusing processed wastewater.
Scientists from IISc (Indian Institute of Science) and CST (Centre for Sustainable Technologies) joined forces and devised a decentralized sewage recycling and treatment plant at an elementary school, located in the distant village of Berambadi, Karnataka. This treatment plant has facilitated the conservation of 180,000 liters of water annually. For the last year, this recycling unit helped in reusing wastewater and abated the dependence on freshwater reserves. The project has been performed in association with scientists from Britain.
IISc press release reports that the investigation crew carried out the pertaining project for a year with the assessment of various biological and physicochemical factors of wastewater at both in and out ports. Performance analysis employed parameters such as Faecal
Coliforms (FC), Chemical Oxygen Demand(COD), Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD), total phosphorous, nitrate, Total Suspended Solids(TSS), and Removal Efficiencies (RE). After the assessment, the analytic factors were measured beyond 90% with dominance in RE. The capacity of the treatment unit was 667 liters of wastewater per day, preserving an annual quantity of 180,000 litres.Lakshminarayana Rao, assistant professor, CST, and senior writer of the article issued in Journal of Water Process Engineering stated that their project proved that decentralized sewage treatment plants can be established and implemented in a village area in a cost-effective manner for the first time.
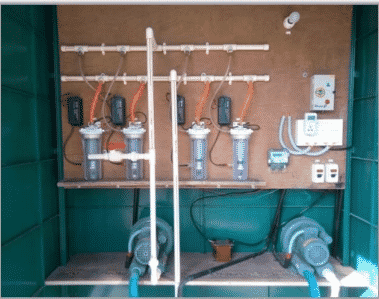
The initial processing begins with the filtering of food chunks with special sieves within the water collected from hand wash sinks. PS Ganesh Subramanian, former project assistant, CST, and lead author of the article, elucidated that the water subsequently moves through three anaerobic sand bio-strainers. These are reservoirs packed with locally accessible sand, medium, and coarse gravel, in which microbial biofilms promote the catabolism of nutrients present in sewage to decrease the nutrient content of water.
The sewage collected from kitchen sinks is initially filtrated through a grease trap to remove the oil and grease from the surface layer. Later, water is allowed to enter an anaerobic sludge bioreactor and stratified biofiltration compartment. In the end, the strained water from all the sinks (hand and kitchen sink) is transited to ozonation and aerations chambers, where water is processed with ozone for sterilization. The processed water contained in an overhead reservoir is then immediately usable for domestic non-potable applications like flushing toilets and gardening by the staff or students of the school. Subramanian claimed that the process of ozonation eliminates the smell and color of the sewage, removes FC, hence sterilizing the water with no release of harmful intermediates. It also boosts the DO level of the water
Central Pollution Control Board claims that India will require 1.5 trillion m³ water by 2030. From where India can access water in the upcoming years. This treatment plant can be a remedy for this conundrum.
The rural inhabitants of Berambadi are extremely satisfied with the novel sewage treatment plant. Looking at the huge achievement of the project, many schools in Karnataka have contacted them to establish a replica in their schools as well, Rao revealed.
Author: Geema George






























