Human ancestral family tree clarified from the oldest human genetic evidence
800,000-year-old human fossil tooth retrieved for the first time has paved the way to obtain genetic information and human ancestral family tree.
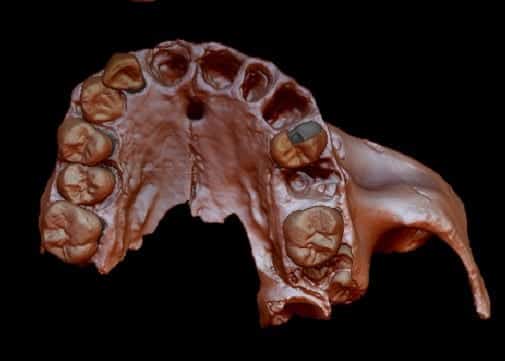
This has made it possible for researchers to map the human ancestral tree further back than ever – as well as settle a long-standing debate on evolutionary.
The research study by the University of York recovered the oldest human genetic data set from a tooth found in Spain of a species ‘Homo antecessor’.
Protein
The researchers confidently determined the position of Homo antecessor in the human family tree by sequencing ancient proteins from dental enamel using a method called mass spectrometry.
The proteins were analyzed to determine if the healthy protein was original by Dr. Marc Dickinson and Dr.Kirsty Penkman, Department of Chemistry.
Tooth enamel of 2 hominin varieties, one 800,000-year-old (Homo antecessor), and one 1.77-million years of old (Homo erectus) were analyzed in this research by the Copenhagen team. But it was extremely difficult to obtain protein sequence data from the Homo erectus, so the York team utilized their experience in evaluating ancient proteins to determine whether the protein was original.
Dr
. Marc Dickinson and Dr. Kirsty Penkman determined that the proteins present in the Homo erectus enamel were original using the predictable destruction paths of amino acids and proteins, but the proteins showed very high levels of degradation.The order of the amino acids in the protein chain allows evolutionary relationships to be unpicked. However many of the amino acid links were broken down in Homo erectus, implying that most of the sequence information had been lost. But, the proteomics sequence information produced by the Copenhagen team can be confirmed by assisting this data.
Millions of years
“Finding the original organic material, which has made it through for countless years is fascinating. It is unbelievable that these examples are still able to provide scientific information so long after their formation,” said Dr. Marc Dickinson.
The lineages of humans and chimpanzees split from each other for about 7-9 million years. Yet researchers wished to comprehend much better the evolutionary relationships between our species and others, all currently extinct, in the human family tree.
Preliminary studies led to decide that Homo antecessor was the last common ancestor to modern human beings and Neanderthals. The specific relationship between Homo antecessor and various other human groups, like ourselves and Neanderthals, has actually been long disputed.
Facial features
Current researches verified that the facial characteristics of Homo antecessor are really comparable to those of Homo sapiens as well as very different from those of the Neanderthals and their recent ancestors.
The analysis of these old proteins from the 800,000 year-old-tooth gives additional proof that there was a close relationship between Homo sapiens and Homo antecessor.
“Ancient protein analysis provides evidence for a close relationship between Homo sapiens, Homo antecessor, Neanderthals, and Denisovans,” said Frido Welker, First author, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Globe Institute, University of Copenhagen.
“The outcomes of our study sustain the idea that Homo antecessor was a sibling group to the group having Homo sapiens, Denisovans, and Neanderthals.”
As a result of the chemical degradation of DNA with time, the oldest human DNA obtained so far is dated at no more than approximately 400,000 years. However, the analysis of ancient proteins by a technique called palaeoproteomics using mass spectrometry has actually made it possible for researchers to surmount the limits.
Author: Sruthi S






























