New Antibacterial Food Coating
RUDN University chemists have developed a convenient and straightforward method for producing derivatives of the natural polymer chitosan.
These derivatives are non-toxic and have a high antibacterial activity which can combat common bacteria. According to scientists, these substances can be used in the production of antibacterial protective films for food.
Preservatives- primarily chemicals, are widely used ascross the food industry. They are critical to extending the shelf life of products. Contrary to this, these preservatives reduce food quality.
Some of the chemical preservatives, such as benzoic acid, can even cause allergies. Synthetic waxy substances such as biphenyl used to coat fruits are considered to be carcinogens. Biphenyl is prohibited in the United States and the European Union. These data explain the importance of finding new preservatives that are effective and safe.
New Antibacterial Food Coating- Azido Chitosan
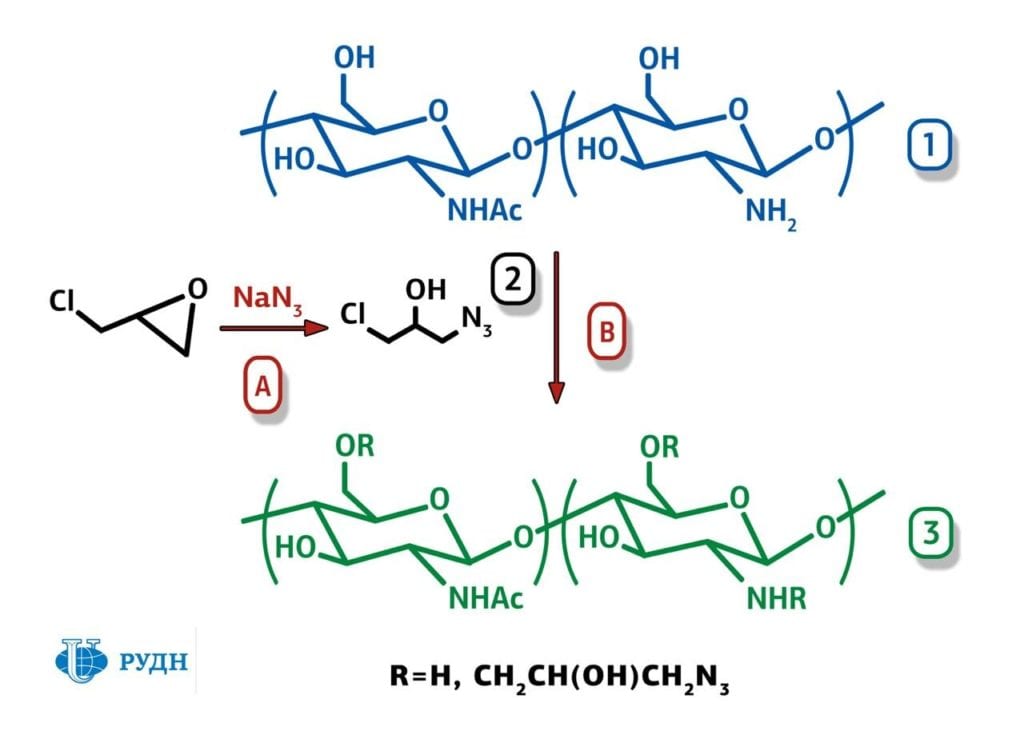
Chitosan is a natural polymer derived from chitin. It is the main component of insect and shrimp shells.
It has antibacterial properties and is already used in the food industry for packaging and coating products with a protective film. However, the conventionally used Chitosan does not have the antibacterial property at par with antibiotics.
Andreii Kritchenkov and Margarita Kurasova, RUDN University
chemists along with a team of scientists, modified chitosan with organic azides. This was done by sewing them to the polymer chain. Azides are derivatives of hydrazoic acid. Both natural and inorganic azides are toxic. Though their compounds with chitosan are considered safe. Antibacterial activity of the obtained substances- azido chitosan, was significantly higher than that of chitosan.The study showed that samples of polymers based on chitosan had antibacterial activity comparable with that of antibiotics. The researchers compared this parameter for azido chitosan with the two commonly used antibiotics— gentamicin and ampicillin.
New Antibacterial Food Coating- The Experiment
Antibacterial activity was determined by diffusion into the agar layer- same as the commonly used Disk Diffusion method. A disk of filter paper impregnated with the test substance or comparison antibiotic was placed on the agar plates containing the bacterial culture. The content (antimicrobials) penetrates the agar, killing bacteria or slowing their reproduction.
Consequently, a zone of inhibition formed around the disk. The value of the antibacterial activity is estimated by the diameter of the area of inhibition. A standard colorimetric test determined toxicity.
Azido Chitosan- the New Antibacterial Food Coating prevented Staphylococcus aureus growth in a zone of 26 mm in diameter- the benchmark by ampicillin was 30 mm. For E. coli, the zone of inhibition by azido chitosan was measured to be 26 mm in diameter- the reference using gentamycin was 22 mm.
This experiment demonstrated that the polymer has almost the same antibacterial activity as antibiotics. This is a significant finding as antibiotics as components of antibacterial films is highly unacceptable because it leads to the development of resistant strains of bacteria.
New chitosan derivatives can be used as safe and effective preservatives to create protective films for food on this basis.






























