The New Era of mRNA Vaccines and AI-Powered Therapeutics
Introduction:
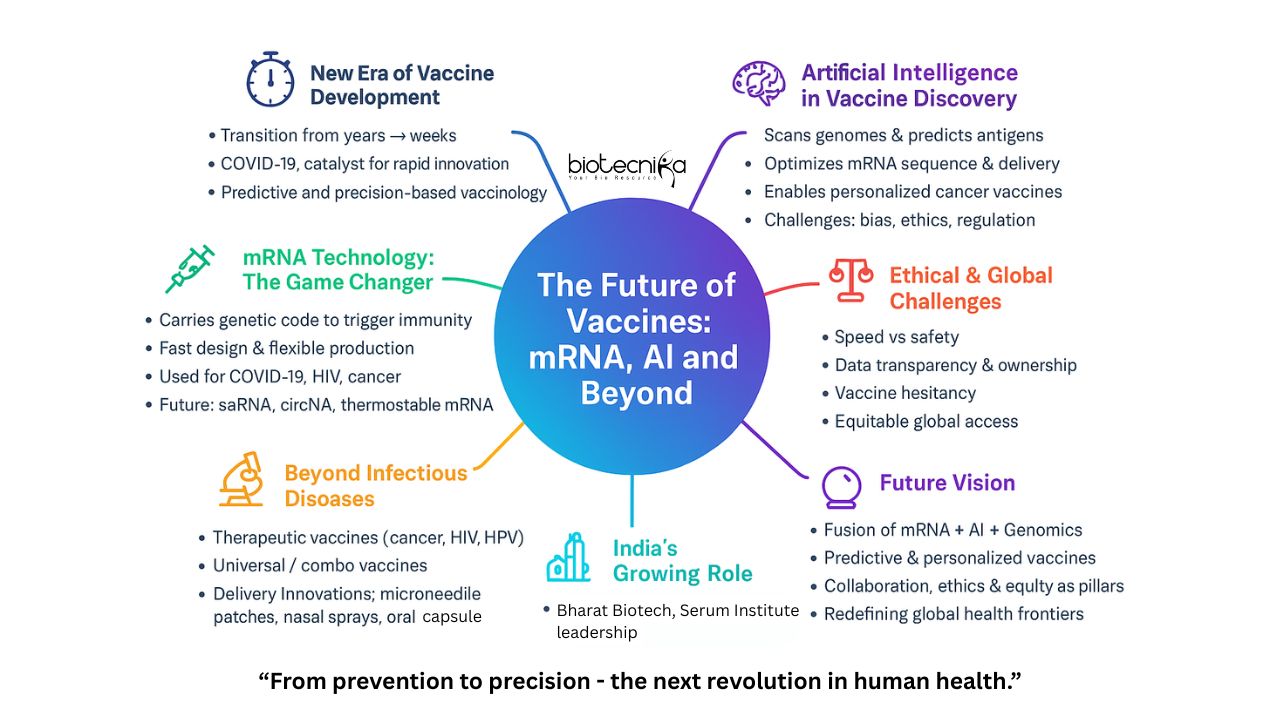
The vaccine development process is entering a new era, where from traditional methods that took years to innovations that accelerate discoveries within weeks to months. This field is evolving rapidly with breakthroughs like mRNA vaccine technology, advanced bioinformatics, and artificial intelligence. The future of vaccines is not only evolving rapidly, but also it is evolving in a smart and more precise way, which is laying a foundation for how the world responds to novel diseases.
The COVID-19 pandemic changed the perspective of how the medical and therapeutic sector was looked upon. Once, vaccine development took about years to decades, but it has been proven that vaccines can be developed at a remarkable speed. By decoding the genome of the virus using mRNA technology, scientists could design and produce a new vaccine within weeks. This stands out as a historic revolution in the manufacturing of vaccines.
Now that mRNA technology meets Artificial Intelligence (AI), and with the combination of computational biology and Next-Generation Sequencing advancements, it opens new possibilities for faster and precise vaccine development. There is extensive research going on across the world to find new ways in which vaccines and personalized medicines can be produced. A few Life Science and Pharma giants have teamed up to pool the data and develop an AI Model that accelerates drug discovery.
The real challenges arise when science advances! From Lab to Market, the journey is vast. Understanding the intersection of biology and technology, tailoring vaccines according to the locality and the intensity of the condition is essential. Together, these technologies are shifting vaccine research from a reactive process to a predictive and precision-driven step. As vaccinology is evolving, it is expanding towards other conditions like cancer, rare and neglected diseases, and is not limited to viruses.
The mRNA Vaccine Revolution: A Blueprint for Faster, Smarter Vaccines
Messenger RNA or mRNA is the molecule that carries the genetic information about which protein to make. This information is used by the scientists to design new vaccines. Traditional vaccines rely on weakened or inactivated viruses to trigger immunity. In contrast, mRNA vaccines deliver genetic instructions that tell our cells to produce a harmless fragment of the target pathogen, prompting the immune system to respond (such as the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2).
This approach offers unmatched speed, flexibility, and adaptability compared to other methods. Once the target antigen is identified, an mRNA vaccine can be designed and produced within weeks. This step proved the efficiency during COVID-19 and now serves as a model for future outbreaks.
But the true promise of mRNA goes far beyond COVID-19. Vaccines are being developed by researchers against influenza, Zika, HIV, RSV, and even malaria. In oncology, therapeutic mRNA vaccines are being designed in a way that aids the immune system to recognize and attack tumors, making them personalized for each patient.
Innovations such as self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) and circular RNA (circRNA) could increase the vaccine’s potency and longevity, while thermostable formulations may solve the cold-chain problem that limits global access. The challenges still remain in durability in the immune system, large-scale manufacturing, and equitable access in low-resource settings. Yet, each challenge drives a new wave of biotech creativity, one that continues to redefine what vaccines can do.
Artificial Intelligence: The Silent Engine Behind Vaccine Discovery
If mRNA is the new language of vaccines, AI is the translator; turning genetic codons to computer codes, accelerating its progress. From identifying promising antigens to predicting immune responses and optimizing molecular design, AI assists scientists at every step.
AI-driven algorithms can scan pathogen genomes in hours, identifying potential epitopes (immune-activating sites) that traditional methods might overlook. Deep-learning models like LinearDesign are being used to refine mRNA sequences for greater stability and protein expression.
Beyond design, AI is also improving formulation and delivery. Machine learning models simulate how lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), the carriers for mRNA, behave in the body, helping researchers craft safer and more efficient delivery systems.
We can tell that one of the best uses of AI is in personalised medicines. By analyzing a patient’s tumor genetics, AI can predict which neoantigens will trigger a strong immune response, allowing researchers to custom-build a therapeutic vaccine unique to that individual. AI also enhances manufacturing and logistics from predicting raw-material shortages to optimizing cold-chain routes.
However, the technology comes with scientific and ethical challenges. Data bias, lack of transparency (“black box” problem), and limited regulatory frameworks raise questions about accountability and reproducibility. The AI-developed vaccines still require preclinical and clinical testing.
Beyond Infectious Diseases: Expanding the Vaccine Outlook
Unlike earlier, vaccines are not just confined to preventing infectious conditions, they have crossed the boundary and now entered to treat diseases and modify the immune responses. Therapeutic Vaccines have become the frontier in treating diseases rather than just preventing them. These vaccines are designed in a way that detects where the ailment is and reprograms the immune system, especially in cases of cancer and other chronic viral infections like Hep-B, HIV, and HPV. Researchers are also working on universal or multi-pathogen vaccines, such as a broad-spectrum flu vaccine or combined flu-COVID shots that could eliminate the need for timely booster doses. Examples include BioNTech’s mRNA-based cancer vaccines (in Phase II/III trials for melanoma) and Moderna’s personalized mRNA vaccine for cancer (mRNA-4157), developed with Merck, which showed promising results in reducing melanoma recurrence.
New innovations have been achieved in vaccine delivery methods to make it easier and more accessible, especially in the low-income regions.
Few of the examples are stated below:
- Microneedle patches (e.g., Vaxxas, Micron Biomedical) allow painless, self-administered vaccination and eliminate cold-chain storage needs.
- Nasal spray vaccines (e.g., Bharat Biotech’s iNCOVACC) stimulate mucosal immunity, the body’s first defense barrier.
- Oral capsule vaccines are still being developed for cholera and COVID-like pathogens.
As an advantage of this novel innovative vaccine, the dependency on the trained medical staff comes down with rise in the global vaccination drives. Understanding immunology much more deeply, opens new ways to regulate immune disorders, allergies, and other conditions like aging as well.
Ethical, Regulatory, and Global Challenges: AI & mRNA Vaccines
Every technological leap comes with responsibility. The speed of mRNA vaccine and AI-driven vaccine development raises new ethical and regulatory questions. How do we ensure safety when algorithms design vaccines faster than traditional testing cycles? Who owns the data used to train these AI models?
Ensuring equal access to all remains a challenge. While high-income countries rapidly adopt next-gen vaccines, many developing regions still struggle with cold-chain infrastructure and distribution. Without global cooperation and transparent technology transfer, innovation risks deepening existing health divides.
Vaccine hesitancy is another barrier. New technologies often spark skepticism, highlighting the need for clear communication, transparency in trials, and public education on how these vaccines work.
The future of vaccination must therefore balance innovation with trust, ensuring that scientific breakthroughs serve everyone, not just a few.
India’s Role in the Global Vaccine Revolution
The biotechnology research in India is advancing drastically and marking breakthroughs with homegrown companies and their life-changing outcomes.
Following the remarkable recognition in the development of India’s first native vaccine, Covaxin, Bharat Biotech has now entered into Cell and Gene therapies. Its recent launch, Nucelion Therapeutics, is wholly dedicated to Next Generation cell and gene Therapy Contract research, Development, and Manufacturing (CRDMO). Other Indigenous vaccines from Serum Institute of India have also transformed the country’s position with respect to healthcare and vaccines.
Indian Institutes and other pharma companies have tied up to research and develop more homegrown mRNA vaccines. They have been expanding their centers in Bengaluru, Pune, and Hyderabad. India is currently focusing on manufacturing and testing therapies and vaccines locally that can cut down the dependency on imports and delays of regulatory approvals, according to the native patients’ profiles. This can improve the career opportunities in the field and encourage more young talents in bringing out the new ideas and development strategies.
With government support for biotech infrastructure and regulatory modernization, India can turn its scale advantage into a science-driven leadership role, producing vaccines that are faster, smarter, and accessible to the world.
Conclusion
The convergence of mRNA vaccine technology and Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing vaccine development, making it faster, smarter, and more personalized. Beyond preventing infections, vaccines are evolving to treat cancers and chronic diseases through precision-driven, therapeutic approaches. The next frontier lies in integrating genomics, AI modeling, and biotechnology to create adaptable mRNA vaccines that anticipate future health challenges. To ensure global impact, innovation must align with ethical responsibility, equitable access, and strong collaboration. With its advancing biotech ecosystem, India is well-positioned to lead this new era, where science not only prevents disease but also redefines the future of human health.