Table of Contents
A Day in the Life of a Stem Cell
Stem Cell Biology, Understanding the Misunderstood Cell.
If you ever feel worried about your life’s decisions or are always in a dilemma as to what to wear, what to eat, what to study, or what career to choose, just think about the cells that lie within you. Stem Cells, the most confused cells ever, are constantly struggling with which path to take. While most cells have a fixed identity and purpose, the stem cells wake up with uncertainty and wonder what to do next.
This article talks about the amount of pressure the stem cells have on themselves, potential yet unsure of what’s next, until proper guidance. Interestingly, these are the most brilliant and powerful cells created by nature, yet they exhibit a sense of indecisiveness.
Welcome to the day of a Stem Cell, see how life takes turns.
Morning Scenes: The Identity Crisis Begins
Every cell in the body has a specific role to play. As soon as they wake up, their job is already designed. For instance, a nerve cell gets busy sending signals, while the muscle cells stretch a bit here and there, and the stem cell at the back of the room is thinking about which team to join or whether to undergo self-replication. If there is a ranking for indecisiveness, our stem cells would be at the top!
Yet beneath this confusion lies enormous power. To understand why we first need to know what stem cells are.
So, What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are omnipotent cells that can take on any form of a cell and its function. This makes them unique and serves as the foundation for every other type of cell in the body. They can divide for long periods, maintain their population, and, under the given conditions, transform into specialised cells with specific functions, such as neurons, muscles, or other types. This ability makes it valuable, as it allows and to choose fate or differentiate.
Unlike other mature cells, which have fixed identities, stem cells exhibit a specific feature called plasticity. In Stem cell biology, stem cells are identified with two defining characteristics:
- Self-renewal: Through repeated cell division, they can create identical copies of themselves
- Potency: The ability to become one or more specialised cell types, under favourable conditions.
These abilities enable the stem cells to be assigned to any branch depending on the body’s needs. Whether the body needs a fresh set of cells after an injury or needs some extra cells during early development, stem cells are always in the first place. Their flexibility is not a sign of uncertainty; it is a complex strategy in our biological system that requires constant repair and renewal.
Types of Stem Cells: Degrees of Confusion and Capability
The stem cells don’t fall under a single category; they are classified into different types of stem cells based on their potency. There are primarily three types of Stem cells:
- Embryonic Stem Cells (Pluripotent)
Derived from the early embryos, these are the most versatile stem cells ever known. They can become any of the 200-plus cell types in the human body. Their potential is vast, which is the reason they are the main focus of developmental research.
- Adult Stem Cells (Multipotent)
These cells have a limited range and are found in tissues like bone marrow, skin, liver, etc. This means a Blood stem cell can give rise only to its lineage, i.e., RBCs, WBCs, and Platelets, but not muscle fibres or neurons. Adult stem cells are limited to certain conditions and can’t achieve beyond that.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
These are the type of stem cells created by human intervention. Adult stem cells are reprogrammed back to a pluripotent state, which almost behaves like an embryonic stem cell, having the freedom to convert into any type according to the conditions. This technique has opened a new frontier in regenerative medicine.
Together, these lay the foundation for stem cell biology – the understanding of stem cells and their abilities.
Mid Morning Hours: Stem Cell Biology of Signalling, and many more…
We can truly become ourselves when we are surrounded by our people, in the same way the stem cell’s day is shaped by its microenvironment, also known as the “stem cell niche”. This niche is composed of neighbouring cells, proteins, chemical signals, and physical structures that guide the behaviour of the stem cells. The niche provides stability as well as a constant push towards the specific task to be performed.
The stem cells are exposed to various factors, including growth factors, hormonal cues, mechanical pressure, nutrient availability, surrounding cell communication, and several molecular pathways. All these inputs influence the fate of the stem cell: whether to remain undifferentiated or to commit to a specific lineage. The process is quite complex and reflects the truly dynamic and responsive nature of stem cell biology.
That Moment of Commitment! Differentiation and Specialization
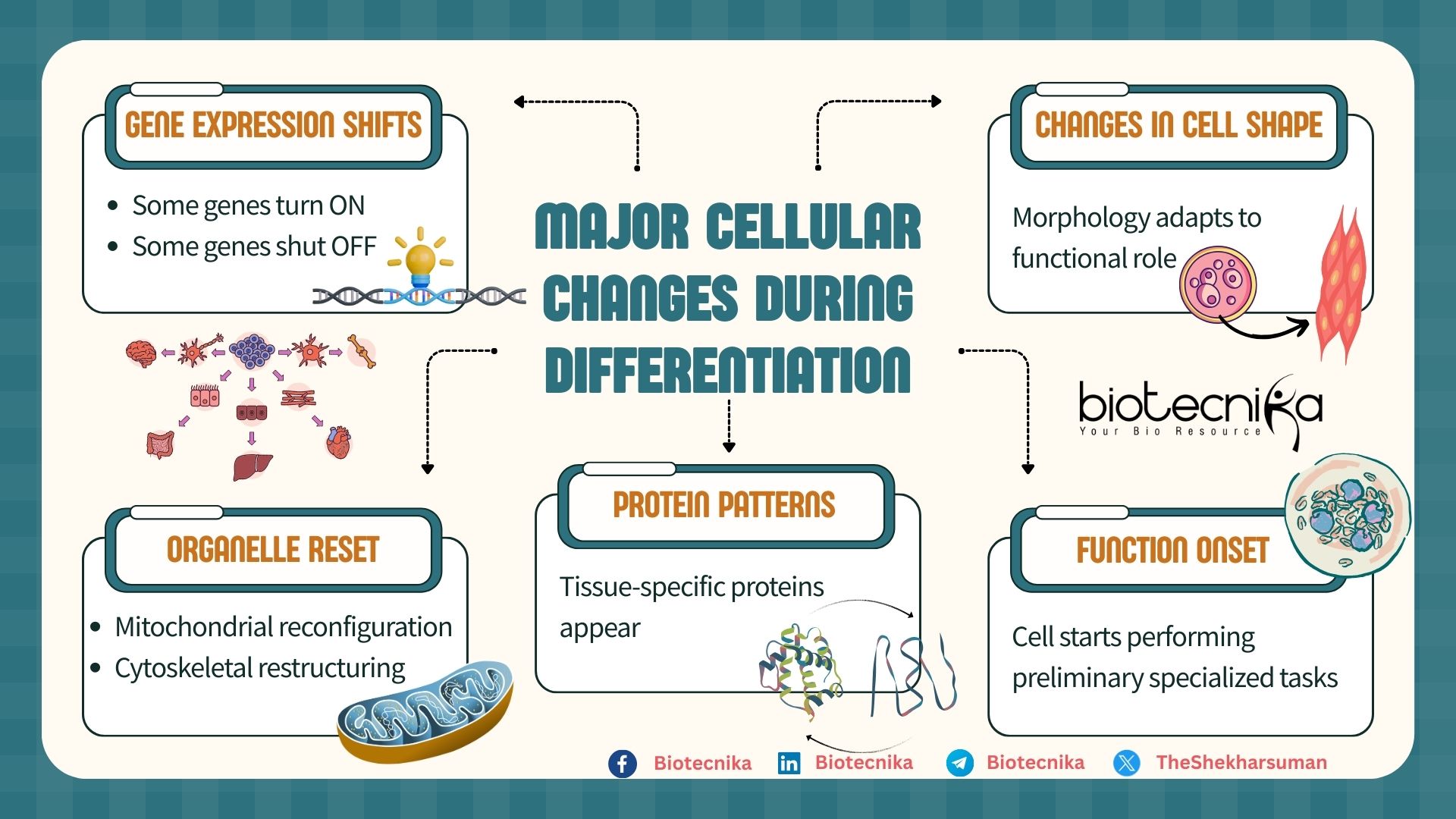
Differentiation and Specialization are both well-orchestrated events. Once the signals are received and the internal switches activate, at that moment the cell has to decide about its future: to remain as a stem cell or to differentiate and specialize. Differentiation is a controlled process marked by various transformations like the on and off of the genes, changes in the cell shape, reorganization of organelles, new patterns in protein expressions, and defined function.
Once the differentiation has concluded, the stem cells now have fixed lineage and functionality, and they can never be in that versatile and flexible state, unlike before. This stage is specialization.
Now, the commitment is for life. Once opted to become a neuron, it can’t change its decision to become a skin cell later. A heart cell cannot become a blood cell. The stem cell got an identity!
Miscommunications leading to Confusion! The Stem Cell Regulation Problem
Stem cell biology is a strictly organised event; the differentiation and specialization occur with remarkable accuracy. But confusion and miscommunication within the niche can lead to serious consequences.
Potential issues include:
- Abnormal Cell Division – The cell takes the wrong path and ends up in a different lineage or form incorrectly.
- Stem Cell Depletion – A large number of cells differentiate at once, leaving insufficient reserves for future repair.
- Uncontrolled Cell Division – This can lead to the formation of tumours or contribute to cancers driven by cancer-driven stem cells.
- Failure to respond to injury – Damaged or wounded tissues remain unrepaired or heal poorly due to a lack of correct signal mechanisms.
Since stem cells are involved in almost all processes and influence a cascade of events, even a minor mistake can affect overall health. Stem cell biology is very complicated and accurate.
Good Afternoon! Welcome to the Laboratory Session
Soon after understanding stem cell biology, they are transferred to a laboratory dish. If the stem cell thought its internal environment was challenging, it is onboard with another environment, outside the body. In controlled settings, researchers guide these cells with far more precision, often better than the body can. This is where the applications of the stem cells come into the picture. Stem cells become essential tools for regenerative medicine and therapy.
In the controlled environment, in vitro conditions, stem cells help researchers
- Understand stem cell biology and development
- Study genetic diseases
- Test drugs without Human or animal models
- Model conditions like Cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer’s
Stem cells are also used to grow tiny simplified organs that mimic the real tissues called Organoids, such as liver clusters, brain regions, kidney models, etc. These mini organs allow the researchers to study and understand disease occurrence and drug responses, which is impossible in real organs due to ethical constraints.
Evening Reflections: Regenerative Medicine Stem Cells
As the day passes, stem cells realise their most significant potential and immense responsibilities in Regenerative medicine. Regenerative medicine stem cells are the most vital part of stem cell biology. They treat the body like a self-repairing machine that needs. Interestingly, they remain flexible throughout life, once their path is determined. Regenerative stem cells focus on restoring tissue and organ function, delaying aging and damage.
Another breakthrough in regenerative medicine is the development of iPSCs, which are the reprogrammed version of adult cells. They behave exactly like embryonic stem cells, hitting the rewind button. iPSCs address ethical concerns and open the door to personalised treatment. The patient’s own cells can be used for tissue grafting, and organs developed with these cells can avoid graft rejection.
How amazing stem cell biology is! The same cell, once accused of not having a clear plan or identity, is now being praised for its potential to become whatever it wants to, according to the needs.
The End Note
A stem cell may spend its day in a state of uncertainty, pulled in different directions by internal and external cues. Yet this lack of a fixed identity is precisely what makes it indispensable. Its flexibility is not a weakness but a superpower, enabling it to build tissues, regenerate organs, and repair damage in ways no other cell can.
While most cells specialize and settle into predictable routines, the stem cell continues to hold open the possibility of transformation. It remains adaptable, responsive, and essential. Its “confusion” is a design feature, not a flaw, but a biological strategy that allows life to renew itself again and again.
Stem cell biology is way ahead of what we think of. Take inspiration from the cells that reside within and go ahead with what is meant for you.