Importance and Career Opportunities in Medical Coding
In today’s fast-moving world healthcare industry, accurate documentation as well as billing are essential to ensure healthcare operations records. Medical coding plays a vital role in this fast-moving era by converting complex medical diagnoses, procedures, and services into standardized codes used for billing and for keeping records. Without Medical coding, healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies would struggle to manage claims as well as ensure proper reimbursement. This article will guide you through its importance, types, and career opportunities.
Understanding Medical Coding
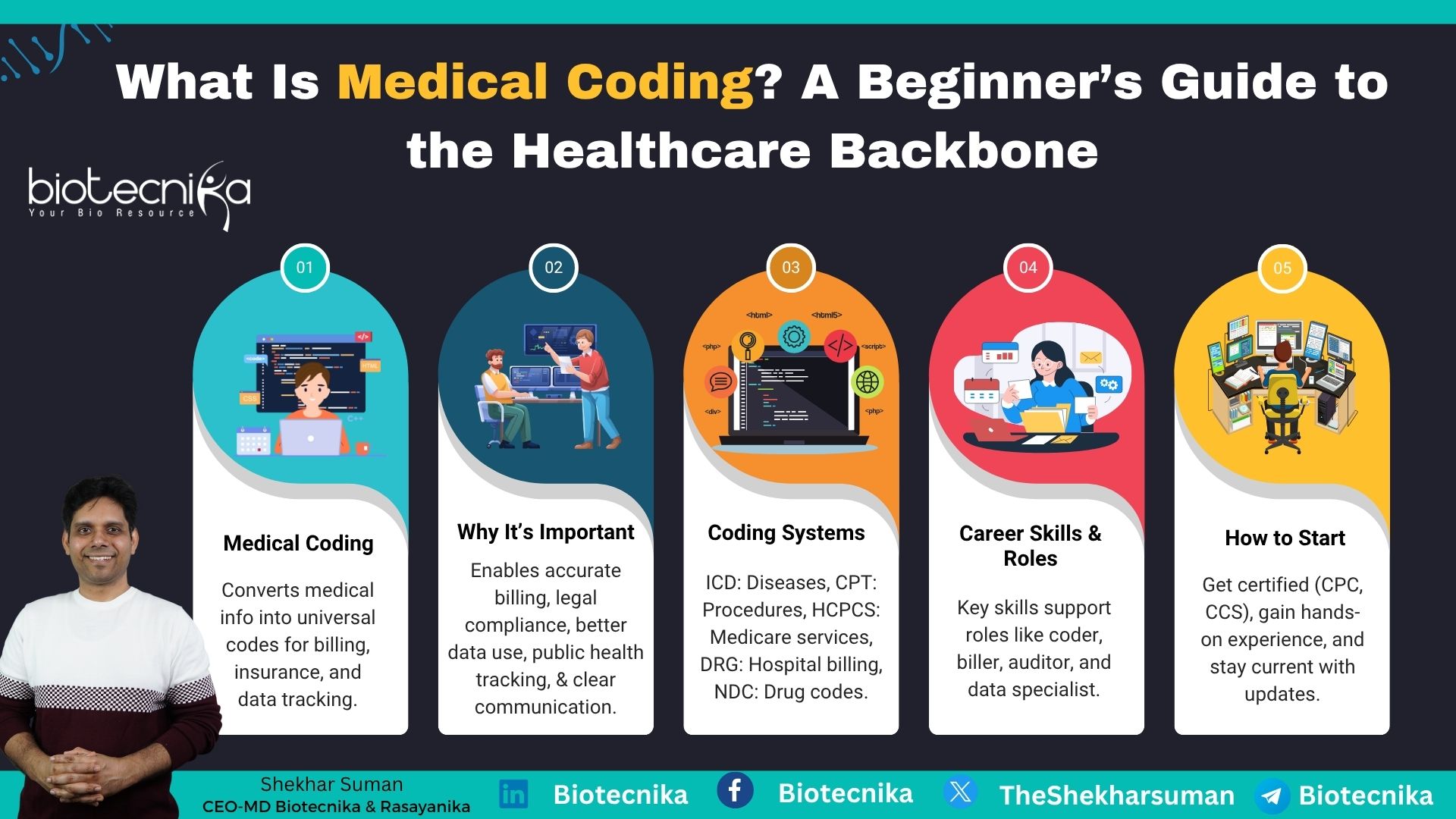
Medical coding is the process of translating healthcare diagnoses, procedures, medical services, and equipment into universal alphanumeric codes. These codes are derived from medical records, including doctors’ notes, laboratory reports, and diagnostic test results. The goal of medical coding is to ensure that healthcare services are recorded accurately for billing, insurance claims, and statistical analysis.
Medical coders play a very important role in healthcare administration. They ensure that provider receive proper reimbursement for their services. They work in hospitals, insurance companies, physicians’ offices, as well as other healthcare facilities. Without proper medical coding, the reimbursement process would be delayed, resulting in financial losses for healthcare providers and administrative burdens for insurance companies.
Importance of Medical Coding
- Accurate Billing and Reimbursement: Medical coding makesure that healthcare providers are paid accurately by insurance companies as well as government programs such as Medicare and Medicaid. This also reduces the errors that could result in underpayment or overpayment.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Proper medical coding helps medical healthcare administrators comply with legal as well as regulatory requirements, reduce the risk of fraud and misrepresentation. Compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act and other regulations is important.
- Efficient Data Management: Proper medical codes help organize and reclaim patient records efficiently, as well as facilitate better patient care and research. It streamlines administrative workflows and improves healthcare analytics.
- Public Health and Research: Medical coding helps healthcare organizations track diseases, treatment methods, and medical trends, aiding research and policymaking. This will also help provide accurate data to support epidemiological studies and healthcare planning.
- Improved Communication: A standardized coding system ensures proper communication between healthcare providers, insurers, and regulatory bodies, reducing misunderstandings and discrepancies in medical records.
Types of Medical Coding Systems
Medical coding depends upon many standardized coding systems. The most commonly used coding system, such as
1. International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
- The ICD system is used for coding diseases and health conditions, and the World Health Organization develops it. The latest version of ICD-11 has updates to classification to accommodate modern medical advancements.
- It is mainly used for morbidity, mortality statistics, insurance claims as well as medical research.
- Example: ICD-10 Code E11.9 – Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Without Complications.
2. Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
- Maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA), CPT codes are used to describe medical, surgical, and diagnostic procedures.
- These codes ensure uniform reporting and billing for healthcare services.
- Example: CPT Code 99213 – Office or other outpatient visit for an established patient.
3. Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
- HCPCS codes are used for supplies, products, as well as services, but not covered by CPT codes; this is specifically used in Medicare and Medicaid billing.
- These include durable medical equipment, prosthetics, and non-physician services.
- Example: HCPCS Code A0425 – Ground ambulance mileage.
4. Diagnosis-Related Groups (DRG)
- DRG codes analyze hospital reports into different groups such as diagnoses, treatments, and patient demographics for the reimbursement process.
- This code is mainly used in hospital billing as well as insurance reimbursement models.
- Example: DRG Code 291 – Heart failure and shock with complications.
5. National Drug Codes (NDC)
- This code is mainly used to identify prescription and over-the-counter medications.
- NCD also ensures precise tracking and billing of pharmaceutical drugs.
- Example: NDC Code 0781-1506-10 – A specific brand of insulin.
The Medical Coding Process
The medical coding process involves several steps to maintain accuracy and compliance in the healthcare sector;
- Reviewing Patient Records: Medical coders analyze laboratory reports and treatment plans to extract relevant medical information.
- Assigning Correct Codes: The medical coder assigns appropriate ICD, CPT, or HCPCS codes based on the documentation.
- Ensuring Compliance: They also ensure that the assigned codes comply with insurance as well as regulatory requirements.
- Submitting Claims: Once coded, the information is used to submit claims to insurance providers for reimbursement.
- Correcting Errors: Medical coders must identify and rectify the issue before resubmission, because sometimes it is denied due to coding errors.
Skills Required for Medical Coders
A successful medical coder must possess the following skills:
- Attention to Detail: Accuracy is critical to avoid billing errors and insurance claim rejections.
- Knowledge of Medical Terminology: Understanding diseases, treatments, and anatomy is essential for accurate coding.
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze medical records and determine the correct codes.
- Computer Proficiency: Medical coding requires specialized software and electronic health records (EHR) systems.
- Regulatory Knowledge: Familiarity with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and insurance policies.
- Communication Skills: Interaction with healthcare providers and billing departments is necessary to clarify documentation.
Career Opportunities in Medical Coding
Medical coding offers a stable and lucrative career path with various opportunities:
1. Certified Medical Coder (CMC)
- Requires certification from organizations like the AAPC (American Academy of Professional Coders) or AHIMA (American Health Information Management Association).
- Provides expertise in applying coding standards across various medical specialties.
2. Medical Billing Specialist
- Focuses on submitting claims and processing insurance payments.
- Works closely with coders to ensure claim accuracy and reimbursement.
3. Coding Auditor
- Review and audit medical codes to ensure compliance with regulations.
- Identifies discrepancies and helps in optimizing billing practices.
4. Clinical Documentation Specialist
- Works with healthcare providers to improve the accuracy of medical records.
- Helps maintain compliance with coding standards and enhances patient data integrity.
5. Health Information Manager
- Oversees medical coding and billing departments in healthcare facilities.
- Implements policies to improve coding efficiency and regulatory compliance.
How to Become a Medical Coder
- Educational Requirement: A high school diploma or GED is required as a basic qualification. However, an associate’s or bachelor’s degree in health information management, medical billing, or a related field can be beneficial. Some institutions also offer specialized medical coding courses.
- Certification: To enhance career prospects, aspiring medical coders should obtain professional certifications such as:
- Certified Professional Coder (CPC) by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC).
- Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). These certifications validate expertise and improve employability in the field.
- Medical Coding Basics Online Training Program from Biotecnika.
Ready to earn up to ₹8 LPA? Medical Coding is calling!
No experience needed – perfect for Life Science grads & freshers
Live CPC Training + 3-Month Project Work + Official Work Letter
Online | 7–8 PM IST | 100% Placement Support
- Gaining Experience: Entry-level coding positions, internships, or on-the-job training programs provide valuable hands-on experience. Many healthcare organizations prefer candidates with practical exposure to medical records and coding software.
- Staying Updated: Medical coding systems and regulations frequently change. Continuous education, attending workshops, and renewing certifications are necessary to stay current with coding updates and industry standards.
Challenges in Medical Coding
Despite its rewarding nature, medical coding comes with many challenges, such as:
- Complex Coding Systems: The continuous evolution of medical treatments as well as procedures requires medical coders to stay updated with new coding versions and protocols, and to keep up with frequent updates in ICD, CPT, and HCPCS codes.
- Insurance and Reimbursement Issues: Medical coders sometimes face issues with claim denials and rejection due to incorrect or incomplete coding. Resolving these issues requires thorough documentation review and resubmission, which can be time-consuming.
- Strict Compliance Requirements: Medical coders must adhere to healthcare regulations, including HIPAA and federal coding guidelines. Any compliance errors can lead to audits, penalties, and potential legal actions against healthcare providers.
- Workload Pressure: They also have to handle a large patient record dataset daily, which can be overwhelming, especially in top hospitals and medical facilities. They should maintain high accuracy as well as efficiency under strict deadlines to avoid claim backlogs and financial losses for healthcare institutions.
Medical coding is important for the healthcare industry, ensuring accurate documentation, billing, and compliance. As healthcare evolves, the demand for skilled medical coders is expected to offer promising career opportunities. It doesn’t matter whether you are looking to start a career in the healthcare sector, administration, or medical coding; it provides a fulfilling as well as rewarding career path. By acquiring the proper education, certification, and experience, you can become a valuable asset in the healthcare ecosystem.