Table of Contents
CRISPR-Cas9: Revolutionizing Genetics and Modern Biotechnology
In 2012, scientists Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier revolutionized the world of genetic engineering with the invention of CRISPR-Cas9, a gene-editing tool that can modify DNA with incredible precision. Their breakthrough was not just a scientific milestone. it sparked a global race to file patents and secure rights over one of the most powerful tools in modern biotechnology. Today, CRISPR is at the heart of treatments for genetic diseases, cancer therapies, and agricultural innovations.
But what protected their innovation from being copied or misused? The answer is patent law.
In biotechnology, where discoveries can lead to billion-dollar therapies or groundbreaking diagnostics, securing a patent is not optional; it’s essential. If you’re a researcher working on anything from synthetic biology to diagnostics, understanding how patent law works could mean the difference between making history or losing it.
This guide, “Patent Law in Biotech: A Beginner’s Guide for Researchers,” will cover everything you need to know about protecting your invention, from the basics of what can and cannot be patented to real-world examples, filing strategies, and global regulations.
What Is a Patent?
A patent is a legal right granted by a government to an inventor, allowing them to exclude others from making, using, selling, or importing their invention for a limited period. It is much like the exclusive right granted for an invention. A patent is given to an inventor for their invention, excluding others from using it for their studies. The government of that particular country usually provides a patent. It is given for a limited period, usually upto 20 years, that starts from the filing date, not the grant date.
Importance of the patent:
- Protecting inventions from unauthorized use for a limited period. If the inventions are readily available, then others can use them for their studies without requiring much effort and may also find new things out of them.
- Patents can be given to genes and DNA sequences, genetically modified organisms, products like vaccines or enzymes produced by fermentation, diagnostic tools, and laboratory tools.
- It helps in boosting the competitiveness of biotech companies where innovation is key.
- It prevents competitors from entering the market with the same strategy and innovation for products and technologies, which helps to maintain a lead.
If you are a researcher in biotech, understanding patent law is key to protecting your work and avoiding legal issues.
Types of Biotech Inventions You Can Patent
A patent cannot be given to everything in biology. There are a few types of inventions in biotechnology that you can patent. A patent is given only when the inventions are,
- Novel – Novel means new, and a patent can be given to new inventions that have not been published before.
- Non-obvious – Patents will be given to inventions that are not an easy or logical next step for someone very skilled in the biotech field. Suppose the patents are easily accessible to experienced people in biotechnology. In that case, they can easily be modulated and used for their studies, making it easy to create new inventions or use those methods to produce valuable products.
- Useful – The invention must have a specific, substantial, and credible utility. This means it should have a real-world application and offer practical benefits, such as improving health, diagnostics, agriculture, or manufacturing.
Typical examples of biotech inventions that can be patented:
- Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering often involves modifying genes, producing synthetic genes, and genetically modified organisms. If these meet the criteria mentioned above, they can be patented.
- Biotech Drugs and Vaccines
In biotechnology, New biologics, enzymes, and vaccines developed using biotech methods are patentable. These products are designed using living organisms, cells, or biological systems to treat or prevent diseases. Thus, they have to be protected.
- Diagnostic Tools
Patents often protect tests that use biomarkers, DNA analysis, or protein-based detection.
A few breakthrough biotech inventions that are patented:
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Recombinant Microorganisms
- Recombinant erythropoietin
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Oncomouse
- Modified Green Fluorescent Protein
- High-throughput DNA sequencing
- CAR-T cells
- CRISPR
What You Cannot Patent in Biotech?
Even if you make a scientific discovery, not everything can be patented. Common exclusions include:
- Natural DNA sequences (not modified), Modified or synthetic DNA sequences may be patentable if they meet the required criteria. Naturally occurring genes, however, are not patentable in many countries including the U.S.
- Laws of nature
- Abstract theories
- Existing plants or animals found in the wild
For example, you cannot patent a naturally occurring gene, but you can patent a modified or synthetic version of that gene.
Why Patent Law Is Important for Researchers?
Biotechnology makes new discoveries and inventions every day. These can be copied and used by others without legal protection.
- Protects Your Research
A patent protects your idea from being copied or used without your permission. This is especially important in competitive biotech research. After being patented, your inventions become legal property. They cannot be used or sold by others without your permission. This protection is crucial in biotechnology, as it involves new products like drugs, vaccines, and genetically modified organisms.
Example: If you create a new method to detect cancer using a gene marker, a patent stops others from copying your method without approval.
- Attracts Funding and Investment
Your patented inventions have several advantages, such as opportunities to raise venture capital or collaborate with biotechnology companies or industries. Patented inventions also lead to increased funding opportunities.
- Helps in Licensing and Royalties
Patented inventions can be license to biotech companies. This will allow them to use your inventions for the studies and in exchange you will get paid for it.
Example: A university researcher patents a novel enzyme. A pharmaceutical company pays to use it in drug development, and the researcher earns royalties.
- Increases Career Value
Patented inventions add value to researchers’ credentials as they show that they have greatly contributed to the research world by adding value and impact to real-world examples.
Want to learn more and become a certified Patent Analyst?
Biotecnika offers an in-depth, hands-on Patent Analyst Training & Certification Program with:
- 6 months of expert-led training
- Real-world project work
- 100% placement assistance
Perfect for biotech students, researchers, or professionals looking to build a rewarding IP career.
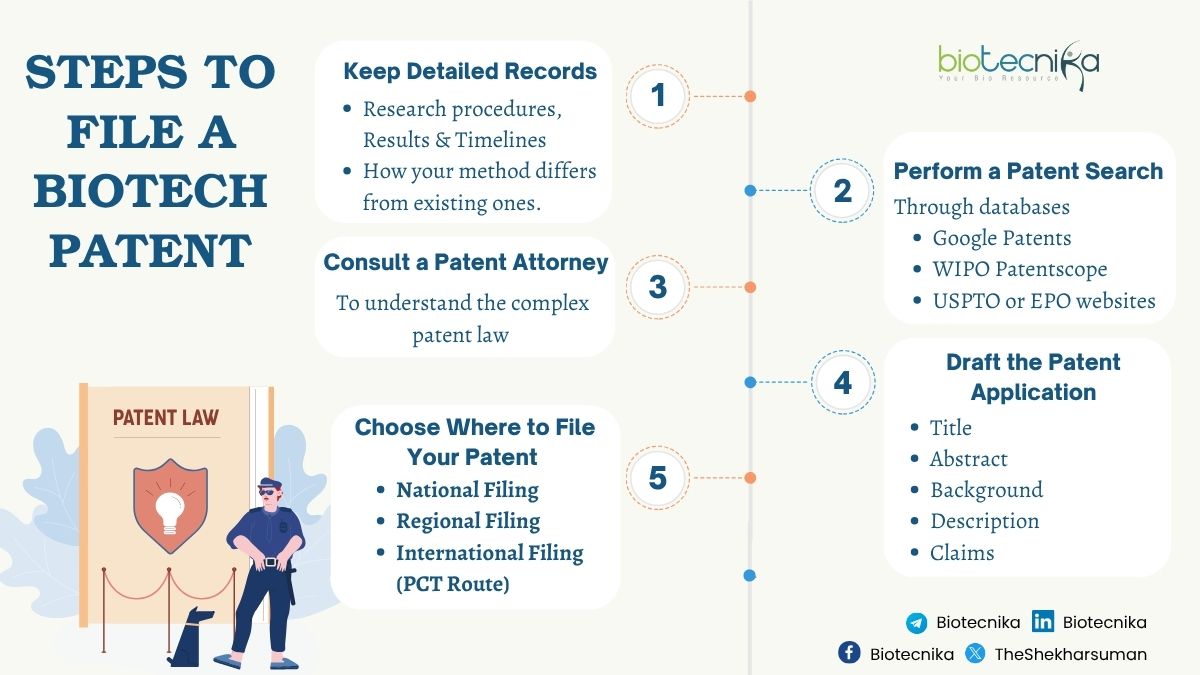
Steps to File a Biotech Patent:
Step 1: Keep Detailed Records
You need to record everything related to your research, including procedures and results. Make notes in notebooks and record timelines of your research work. Document the entire process, including the problem you are solving and how it works. You should also mention why it differs from the existing method of solving the problem.
Step 2: Perform a Patent Search
You must check if the invention you are filing a patent for already exists in the database. Few databases have all the inventions previously made.
- Google Patents
- WIPO Patentscope
- USPTO patent database or EPO websites
These are the few databases where you can check before filing a patent.
Step 3: Consult a Patent Attorney
Biotech patents are highly technical and legally complex. It’s best to get legal advice from a professional who understands biotech. A patent attorney or agent is good at understanding patent law and helps you write strong and accurate patent claims by avoiding legal mistakes, as well as saving time during application review.
Step 4: Draft the Patent Application
Your application must describe the following title for drafting your application.
- Title of the invention
- Abstract: A summary of your invention
- Background: What problem does it solve?
- Description: Detailed explanation with drawings, if needed
- Claims: Define precisely what you want to protect
The claims are the most essential part of the application. They explain what rights you are asking for. Poorly written claims may weaken your protection.
Step 5: File the Application and Choose Where to File Your Patent
Depending on where you want protection, you can file a national (like the Indian Patent Office), regional, or international (like PCT via WIPO) patent application.
- National Filing
For example, file with the Indian Patent Office if you want protection in India.
- Regional Filing
You can file with regional offices like the European Patent Office (EPO) to cover multiple countries.
- International Filing (PCT Route)
The Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) lets you file one international application that covers 150+ countries. This is an excellent option if you want global protection but need more time to decide which countries to enter.
Understanding Patent Claims in Biotech
Patent claims define the scope of protection. In biotech, claims can be tricky. Here are some common types:
- Product claims – Protect the physical product (e.g., a protein or modified gene)
- Process claims – Cover the method used to make or use the invention.
- Use claims – Protect a new use for a known product.
Make sure your claims are clear and detailed. Broad claims offer better protection but are harder to get approved.
Global Patent Laws for Biotech
Patent laws vary by country. Some countries allow certain biotech patents, while others do not. Here’s a quick look:
| Country | Patentable Biotech Items | Restrictions |
| USA | Genes, GMOs, and Biotech Drugs | No natural genes |
| EU | Biotech products, modified organisms | Ethical reviews required |
| India | Biotech processes and modified organisms | India does not allow patents on methods of agriculture or horticulture and diagnostic methods applied to the human/animal body. |
Under Section 3 of the Indian Patent Act, certain subject matters are not patentable in India. This includes:
- Plants and animals in whole or any part thereof (other than microorganisms)
- Seeds and varieties
- Traditional knowledge
- Methods of agriculture or horticulture
- Diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical methods for treatment of humans or animals
These exclusions are in place to protect biodiversity, public health, and traditional knowledge systems from commercial exploitation.
Challenges in Biotech Patent Law
- Ethical Concerns
Some inventions (like cloning or embryo editing) raise ethical questions. These may be rejected or delayed in patent offices.
- Rapid Technology Changes
Biotech evolves quickly. A patent might be outdated before the 20-year term ends.
- Cost of Filing and Maintaining Patents
Patents are expensive. Filing fees, attorney charges, and annual renewal fees add up. This can be a burden for researchers or startups.
Tips for Researchers on Biotech Patents
- File early: Don’t wait too long or someone else might patent a similar idea.
- Avoid public disclosure: Don’t publish your results before filing a patent.
- Work with your institution: Many universities have tech transfer offices to help researchers patent their work.
- Understand your rights: If your research is funded by a company or university, you may not own the patent fully.
Interesting Biotech Patents: Myth vs. Fact
The world of biotech patents is often misunderstood. Here are some common myths—and the facts that debunk them:
| Myth | ✅ Fact |
|---|---|
| You can patent anything in biotech. | Many items—like plants, seeds, and traditional knowledge—are not patentable in India. Even natural substances must be significantly modified to qualify. |
| Filing a patent = full protection. | Filing starts the process, but protection begins only after grant, which may take years. |
| Patents last forever. | A biotech patent lasts 20 years from the filing date—then it’s open to public use. |
| Diagnostic or treatment methods can be patented. | In India and the EU, diagnostic or surgical methods applied to the human/animal body are not patentable. |
| Only big companies file patents. | Not true—students, researchers, and startups can also file, and often do! |
| Once granted, your patent automatically stops others. | You must enforce your patent legally—it gives you the right to stop others, but doesn’t do it for you. |
Today’s researchers must understand patent law, as they will be working on innovations and referring to several other experiments. This will help them protect their latest ideas and contribute to innovations. This guide will help you understand patents and their use in biotech inventions. As a beginner, you need to know all of these things while working on an invention.
Your thoughts and ideas can transform lives in the growing biotechnology field only if protected from others. It is not just for the formality, but also an essential tool for the researcher to turn into a real-world impact.
Whether you’re developing a new gene-editing method, a breakthrough diagnostic tool, or a life-saving biotech drug, knowing how and when to patent your invention can open doors to funding, partnerships, recognition, and long-term success.
As a researcher, you’re already shaping the future of science. Now it’s time to protect that future. Don’t let your hard work go unclaimed. Start learning, start documenting, and take the first step toward safeguarding your innovation with the right patent strategy.






























Great information, I have a fungus which blossoms, into perfect animal s, extinct animals,, perfectly, so it knows Anatomy, Zoology,
Is any one interested in modifying
And patenting ?