Top 10 Biotech Solutions for Global Health Issues
Charles Darwin once said, “It is not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the one most responsive to change.” This statement correctly applies to the field of biotechnology.
The field, once thought to be the weakest, has been the most responsive domain in this era of pandemics, daily rising genetic and chronic disorders, and AI.
Did you ever think AI or Machine Learning would be a part of life science? No right. But life is never what we want it to be; sometimes, it is better than our imaginations.
Well, biotechnology has accomplished things beyond our imagination only because it is responsive to the changing times and has provided us with solutions to some of the most concerning healthcare issues.
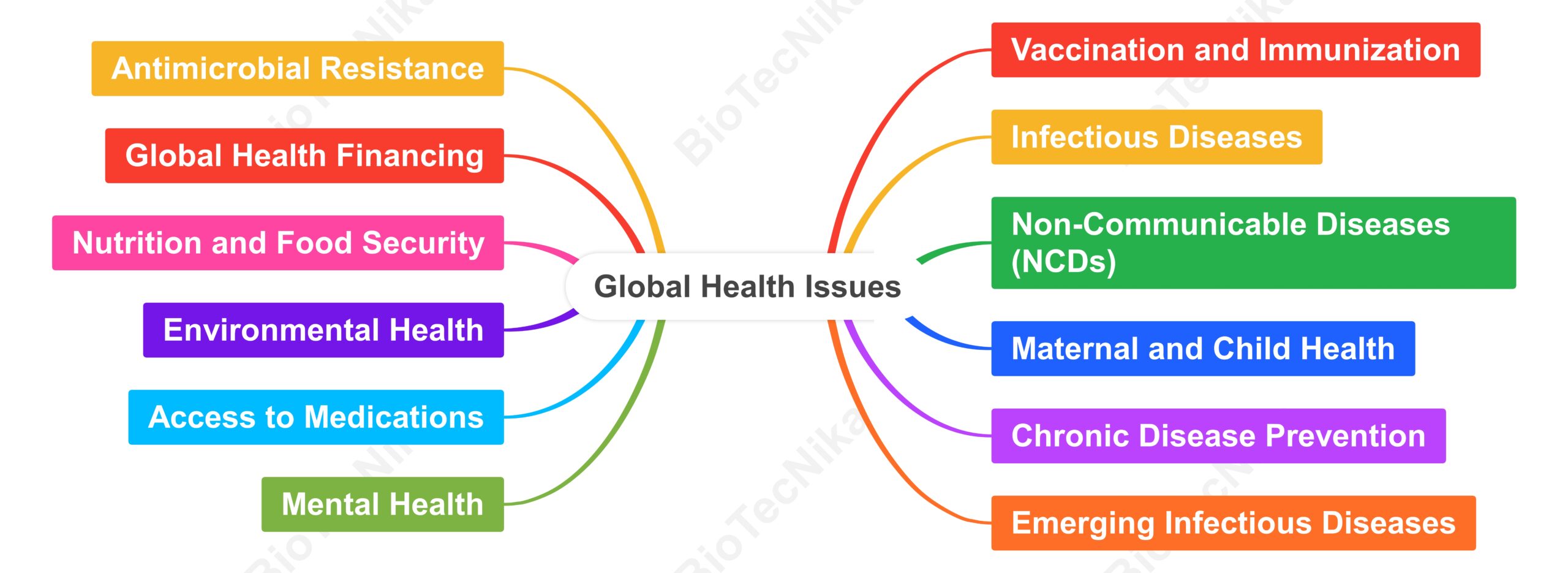
Let’s take a look at the Top 10 Biotech Solutions for Global Health Issues:
- CRISPR gene editing for Genetic Disorders
The most groundbreaking revolution was discovered in 2012 by Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier, the discovery also made them win the most prestigious award, The Nobel Prize in 2020. The discovery was none other than CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology. The technology is capable of precisely editing
genes by cutting DNA at particular sites using the CAS-9 enzyme, which allows scientists to delete, add, or substitute genes of interest into the DNA.Impact on Health: CRISPR is a highly potent technology, it has the ability to cure a wide range of genetic disorders. They can be cured by correcting the underlying mutations that cause the disorder. Diseases that don’t have any permanent cure such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and muscular dystrophy can be effectively cured using gene editing technology. CRISPR can also repair faulty genes, rather than managing symptoms it works on the root cause and cures it completely.
Real-World Example: CRISPR Therapeutics and Vertex Pharmaceuticals have collaborated to work on blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia. According to the clinical trial reports, patients treated with gene editing cells showed considerable improvement, and some have achieved functional cures only after one treatment.
Future Prospects: The range of diseases that CRISPR can cure is enormous. It can not only cure inherited genetic disorders but can also be used to treat cancer and infectious diseases like HIV. With time the technology will become more refined and has the potential to become a universal tool for preventing and treating diseases from their genetic roots.
2. mRNA Vaccines
Vaccines have played a pivotal role in eradicating a lot of diseases that couldn’t be treated normally. We couldn’t survive a pandemic because of vaccines. mRNA vaccine is a revolutionary take on our traditional vaccines which were made of weakened or inactive viruses. The development of mRNA was a turning point in the fight against COVID-19, but its potential ranges up a lot above just pandemics. mRNA vaccines are made of cells with genetic instructions that can produce the viral protein to trigger the immune response.
Impact on Health: One major thing about mRNA vaccines is that they can be developed and produced more rapidly in comparison to our traditional vaccines. This speed is what makes mRNA vaccines essential to combat rapidly mutating viruses, emerging infectious diseases, and global pandemics. Another advantage of mRNA vaccines is that they are highly adaptable and versatile, which allows scientists to use mRNA vaccines to target a wide range of diseases.
Real-World Example: The Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines were the first mRNA vaccines approved for emergency use. The success of these vaccines has led to research for mRNA vaccines for a wide range of diseases, such as influenza, Zika virus, and even cancer, so that the vaccines can be used to trigger an immune response against tumors.
Future Prospects: mRNA vaccines can contribute to healthcare more than you can think of, because of their versatility and scalability. Researchers are exploring if mRNA vaccines can be personalized as per the patient’s requirements and genetic makeup.
3. Monoclonal Antibodies for Targeted Treatment:
Monoclonal antibodies are molecules that are engineered in labs to mimic the immune system’s ability to fight pathogens like viruses and bacteria. They are being extensively used to treat a wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and viral infections.
Impact on Health: Monoclonal antibodies are an extremely targeted line of treatment, they bind to the specific antigens they have been designed for. Monoclonal antibodies bind to the specific antigens on the surface of pathogens or cancer cells to neutralize them, or they mark them so that the immune system can destroy them. The advantage of monoclonal antibodies lies in their specificity, this specificity reduces side effects and enhances the treatment efficacy in comparison to broader-acting drugs.
Real-World Example: In the time of COVID-19, a monoclonal antibody cocktail was developed by Regeneron to treat people infected with the SARS-Cov-2 virus. These antibodies provided passive immunity which helped patients recover faster and reduce the symptoms.
Future Prospects: Researchers are now focussing on developing monoclonal antibodies to treat diseases like HIV, Ebola, and Zika. As antibody engineering is enhanced, we can expect more potent and targeted therapies with fewer side effects.
4. Synthetic Biology: A New Age of Vaccines and Therapies
Synthetic Biology is an emerging field that is a blend of engineering principles and biology, which allows scientists to design and create new biological parts, devices, and systems. Synthetic biology is used for the production of affordable vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostic tools.
Top 10 Biotech Solutions For Global Health Issues
Impact on Health: Synthetic Biology helps in the production of vaccines at a much lower cost and greater scalability. It also facilitates the designing of new biologics that can target diseases that are difficult to treat with traditional methods. It is appropriate for pandemics or tropical diseases, where rapid, affordable, and scalable solutions are required.
Real-World Example: Biotech companies like Gingko Bioworks and Amyris are at the forefront, using synthetic biology to engineer microbes to produce the most widely used pharmaceuticals. These engineered microbes can be used to produce compounds like antibiotics and vaccines with higher efficiency and affordability, making healthcare accessible to all.
Future Prospects: The application of synthetic biology is beyond our imagination. In the coming times, we might see an entirely new class of drugs, personalized vaccines, and novel diagnostics that will completely change healthcare facilities.
5. Personalized Medicine:
Personalized medicine is something that has completely changed our approach toward medicine; it aims to tailor treatments according to patient requirements, genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
Impact on Health: Personalised medicine aims to reduce the trial and error of trying out various lines of treatment to find which is treating the patient best. Our traditional ways of treatment are effective, but understanding which suits the patient best takes up a lot of time, and for diseases like cancer, sometimes the patient does not have so much time. Personalized medicine has the ability to target diseases based on the patient’s genetic makeup and the specific mutations the patient has undergone, which promises better outcomes.
Real-World Example: One of the most pathbreaking advancements made in the field of personalized medicine is CAR-T Cell Therapy, which is a type of immunotherapy where the patient’s T-cells are genetically engineered to attack the cancer cells. Companies like Novartis and Gilead have developed CAR-T cell therapy and have seen massive success in treating certain types of blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
Future Prospects: As we explore more, the use of personalized medicine will go beyond treating cancers; it can also be used for cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and neurological disorders. Another possibility is that in the future, treatments will become entirely personalized and designed as per patient requirements.
6. Telemedicine and AI-enhanced Healthcare
Blending AI with telemedicine has revolutionized the healthcare delivery system, especially with the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, when remote healthcare solutions were required.
Impact on Health: Telemedicine is the bridge between healthcare providers and patients; it offers remote consultations, diagnostics, and treatment plans specifically for rural areas. AI can analyze large amounts of medical data, images, and genetic information and provide faster and more accurate diagnoses.
Real-World Example: The World is making new advancements using AI in healthcare, companies like Tepmus, are using AI to personalize Cancer treatments by analyzing clinical and molecular data.
Future Prospects: As AI becomes more intricately involved in healthcare, it will be more extensively used for disease prevention, early diagnosis, and treatment planning and telemedicine will keep expanding its reach to make healthcare accessible for all.
7. Biotech-Based Diagnostics for Rapid Disease Detection
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, and biotech-based diagnostics have made it possible to do such early diagnosis more accurately than ever before.
Impact on Health: NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) and point-to-cure diagnostics have enabled early detection of diseases like tuberculosis, malaria, and HIV. These technologies have made it much easier and more accurate to diagnose these diseases.
Real-World Example: Cepheid’s GeneXpert diagnostic platform has made a pathbreaking revolution in testing tuberculosis (TB) by providing rapid molecular diagnostics that can be used in remote settings. It has been important in controlling tuberculosis, especially in low-resource areas.
Future Prospects: With time as more advancements take place, biotech-based diagnostics will become more widely available and affordable. Which will allow mass screening for both infectious and non-infectious diseases. This will help in early detection of the disease, and also reduce healthcare costs, and improve the survival rate.
8. Regenerative Medicine:
Regenerative medicine is focused on replacing and repairing damaged cells. This domain works on addressing the global shortage of organs for transplants and finding treatments for degenerative diseases.
Impact on Health: Regenerative medicine uses stem cells to grow new functional tissues and organs, this technique has the capability of growing new organs for the stem cells of the patients, hence reducing the need for donors to donate organs and it can also heal conditions like spinal cord injuries, heart disease or neurological disorders.
Real-World Example: Biotech companies like Organovo are using 3D bioprinting to create human tissues for drug testing, and in the future, it can be used for organ transplants.
Future Prospects: In the upcoming years, as the biotech industry makes more progress, we can expect breakthroughs in organ regeneration, which means damaged organs can be replaced and repaired using lab-grown tissues.
9. Microbiome Therapeutics:
Microbiome therapeutics aim to manipulate the human microbiome to treat diseases that are particularly related to the immune system and metabolism.
Impact on Health: Maintaining a healthy and balanced gut microbiome can treat diseases like IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease), obesity, and mental health issues. Further research has also explored the connection between gut microbiome and autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Real-World Example: Seres Therapeutics is working on developing microbiome-based treatments for Clostridium difficle infections, which are difficult to treat with conventional antibiotics.
Future Prospects: As we understand the microbiome in more detail, microbiome-based therapeutics will become more common. There are possibilities that microbiome therapeutics can offer treatments for various diseases like diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
10. Cell and Gene Therapies for Rare Diseases
Cell and gene therapies have played a pivotal role in addressing rare genetic disorders by treating them from their root cause.
Impact on Health: Cell and gene therapy has provided us with treatments for diseases that were once untreatable. This technique has been beneficial for treating diseases like spinal muscular atrophy and beta-thalassemia.
Real-World Example: Bluebird Bio has developed gene therapies for rare conditions like beta-thalassemia and cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (CALD). These therapies deliver functional copies of the defective or missing genes and offer a permanent cure.
Future Prospects: Over time, as more gene therapies keep getting regulatory approvals and their costs reduce, they have the ability to become standard treatments for a wide range of genetic diseases. The upcoming decade is most likely to see a lot more advancements in gene-editing technologies.
To conclude, we can say that we have come a long way in this journey of revolutionizing healthcare, and there is much more to do. With these groundbreaking inventions, healthcare has completely transformed and has given us hope that no disease is incurable. We might not have solutions to all problems today, but we will in the future.
Latest Article: Top 10 Biotech Solutions For Global Health Issues