CSIR NET Unit 8 Notes Download
Genetics! Unit 8 of CSIR NET life science is all about genetics. A Minimum of 25 marks questions come in the exam from this unit. Thus it’s a strict no to skip this unit. One can expect both theoretical and numerical-based questions, and at times, both combined. The best way to prepare for this unit is to write & practice more & more.
Since CSIR NET June 2022 exam is just around the corner. Biotecnika is here to help you with revisions. Presenting Revision notes for CSIR NET life science UNIT 8.It contains pointers / notes / diagrams/ flow charts for all the important topics.
Reference Books for CSIR NET UNIT 8:
- iGenetics: A Molecular Approach by Peter Russell
- Principles of Genetics by D. Peter Snustad, Michael J. Simmons
- Genes – By Benjamin Lewin
Topics Covered:
- Introduction
- Important terminologies
- Mendel Laws
- PRINCIPLE OF DOMINANCE
- PRINCIPLE OF SEGREGATION
- PRINCIPLE OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT
- Variations involving single genes
- Cross
- PROBABILITY RULES
- Product Rule
- Sum Rule
- BINOMIAL EXPANSION
CSIR NET Unit 8 Notes download
Fill Up the Form To Download Complete UNIT 8 A, B & C notes + Flowchart for Types of Cross
Introduction To Genetics
GENETICS
is the branch of biology that deals with the heredity and variation of organisms.Chromosomes carry the hereditary information (genes)
- DNA -> RNA -> Proteins
- Chromosomes (genes) occur in pairs
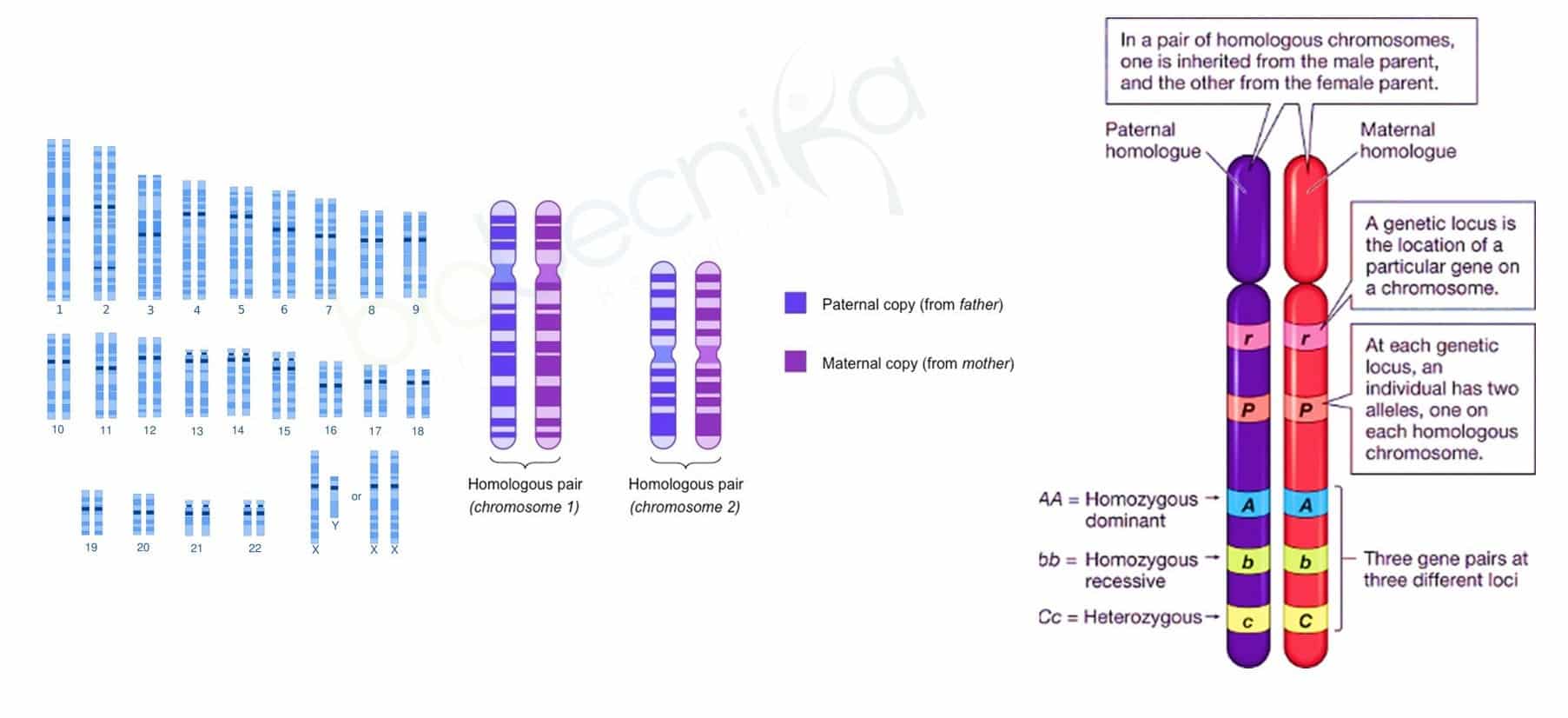
HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES
Homologous chromosomes contain DNA that codes for the same gene.
Terminologies:
- Sister chromatids are two identical copies of the same chromosome formed by DNA replication, attached by a structure called the centromere.
- Gene – Unit of heredity; a section/region of the DNA sequence encoding a single protein
- Genome – Entire set of alleles that an individual possesses
- Alleles – One of two or more alternate forms of a gene
- Two genes occupy the same position on homologous chromosomes and cover the same trait (like ‘flavors’ of a trait).
- Locus –The fixed location on a strand of DNA where a gene or one of its alleles is located.
- Homozygous – Individuals with two copies of the same specific allele of a particular gene are said to be homozygous for that gene.
- Heterozygous – Plants with two different alleles of a particular gene are said to be heterozygous.
- Dominant – Allele of a gene that masks or suppresses the expression of an alternate allele; trait appears in heterozygous condition.
- Recessive – An Allele that is masked by the dominant allele; does not appear in the heterozygous condition, only in homozygous.
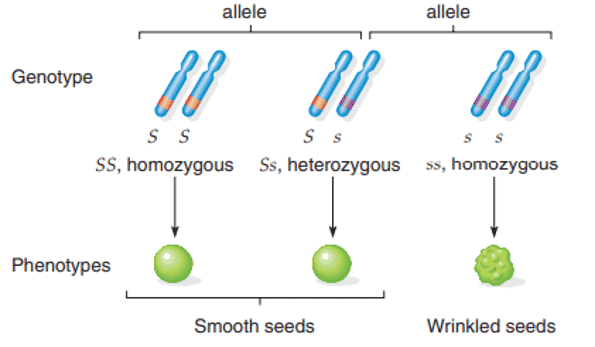
Fig: Dominant and recessive alleles of a gene for seed shape in pea
For example,
- true-breeding, smooth-seeded peas have the genotype SS, and true-breeding wrinkle seeded peas have the genotype ss; both are homozygous.
- The smooth parent is homozygous dominant; the wrinkled parent is homozygous recessive.
- In our example, the S allele was dominant to the s allele, so in the heterozygous condition the seed is smooth. Therefore, both the homozygous dominant SS and the heterozygous Ss seeds have the same phenotype (smooth), even though they differ in genotype.
GREGOR JOHANN MENDEL
- Austrian Monk, Son of a peasant farmer
Fig: Gregor Johann Mendel (1822–84) - At the age of 21 he was admitted to Catholic Monastery in Brunn (Czech Republic).
- Went to the university of Vienna, where he studied botany and learned the Scientific Method
- Began a series of breeding experiments with the garden pea Pisum sativum to learn about the mechanisms of heredity in 1854.
- Completed his experiments in 1864.
- Published his work in 1865 in Natural History Society.
- Developed theory to explain the transmission of hereditary characteristics from generation to generation.
MODEL PLANT: Pisum sativum
- Easy to cultivate
- Had a relatively short life cycle, it Bears flowers and fruit in the same year a seed is planted, producing many seeds.
- Pea flowers contain both male and female organs.
- Pollination of the plant was easy to control.
- Many distinguishable characteristics
SEVEN CHARACTER PAIRS IN THE GARDEN PEA WERE STUDIED BY MENDEL IN HIS BREEDING EXPERIMENTS
Mendel selected seven pairs of traits to study in breeding experiments. Each pair affected one characteristic of the plant, with each member of a pair being distinguishable:
- Flower and seed coat color: grey versus white seed coats, and purple versus white flowers (a single gene controls both these color properties of seed coats and flowers)
- Seed color: yellow versus green
- Seed shape: smooth versus wrinkled
- Pod color: green versus yellow
- Pod shape: inflated versus pinched
- Stem height: tall versus short
- Flower position: axial versus terminal
Some more important Terminologies:
- P generation: Parental generation in breeding experiments.
- F1 generation (First Filial Generation): The progeny of mating of individuals of the P generation.
- F2 generation Second Filial Generation): The progeny resulting from interbreeding F1 generation individuals.
- Genotype: Genetic constitution of an organism.
- Phenotype: The physical manifestation of a genetic trait results from a specific genotype and its interaction with the environment.
- True-breeding: A trait studied remains unchanged from parent to offspring for many generations.
Mendel Laws:
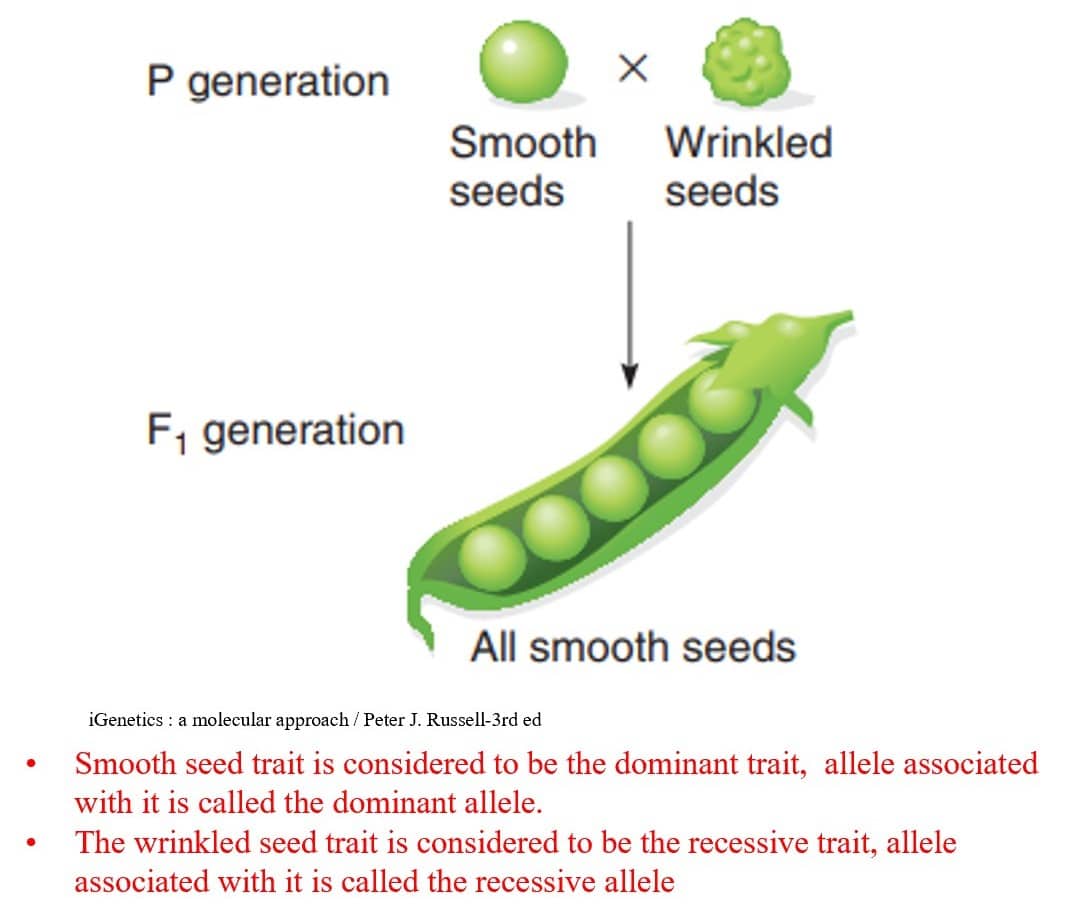
PRINCIPLE OF DOMINANCE
- In a heterozygote, one allele may conceal the presence of another.
- In a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation.
- All the offspring will be heterozygous and express only the dominant trait.
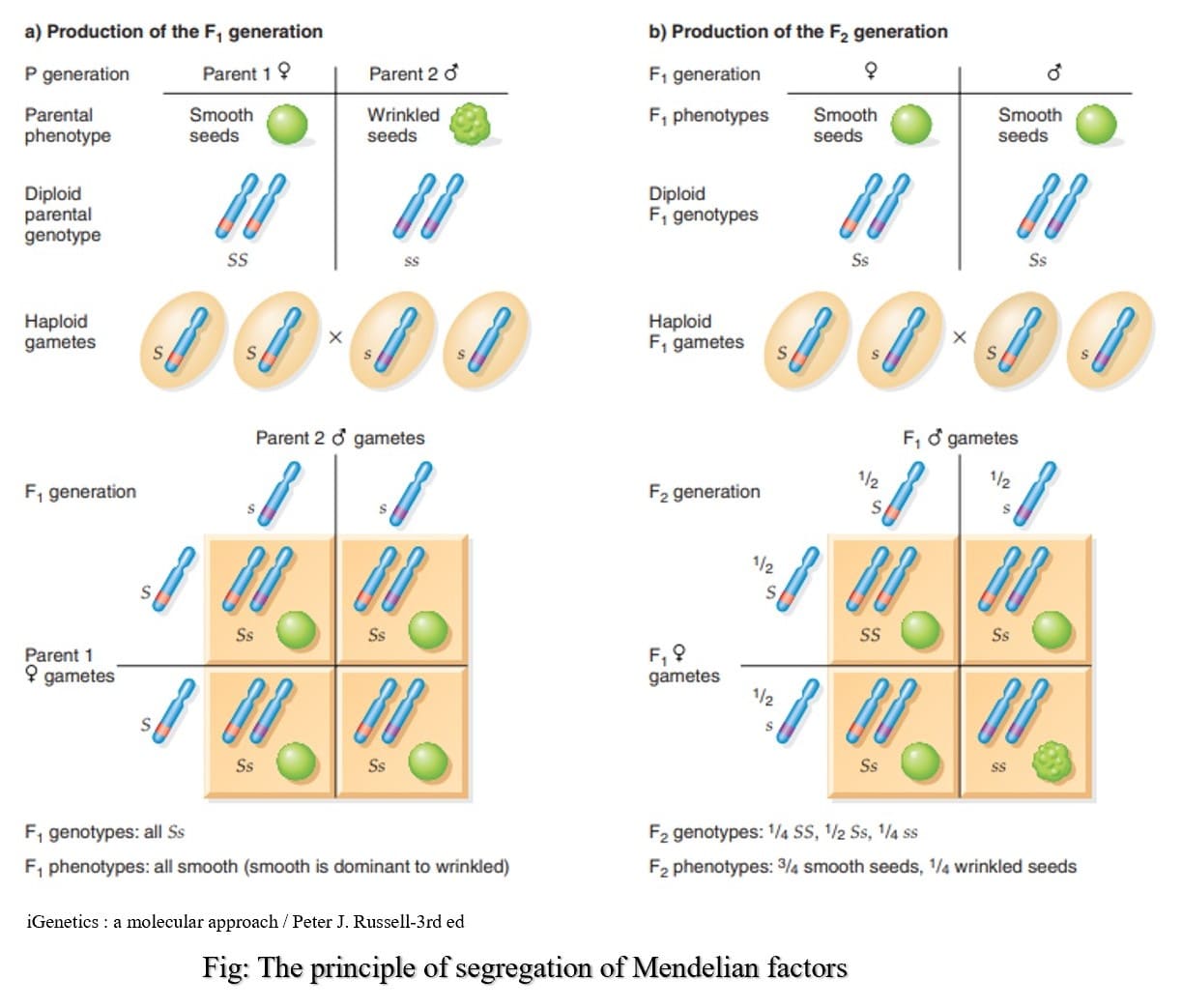
PRINCIPLE OF SEGREGATION
- Law of purity of gametes
- The two members of a gene pair segregate from each other during the formation of gametes in meiosis.
- As a result, half the gametes carry one allele, and the other half carry the other allele.
- Recessive traits, masked in the F1 from a cross between two true-breeding strains reappear in a specific proportion in the F2.
PRINCIPLE OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT
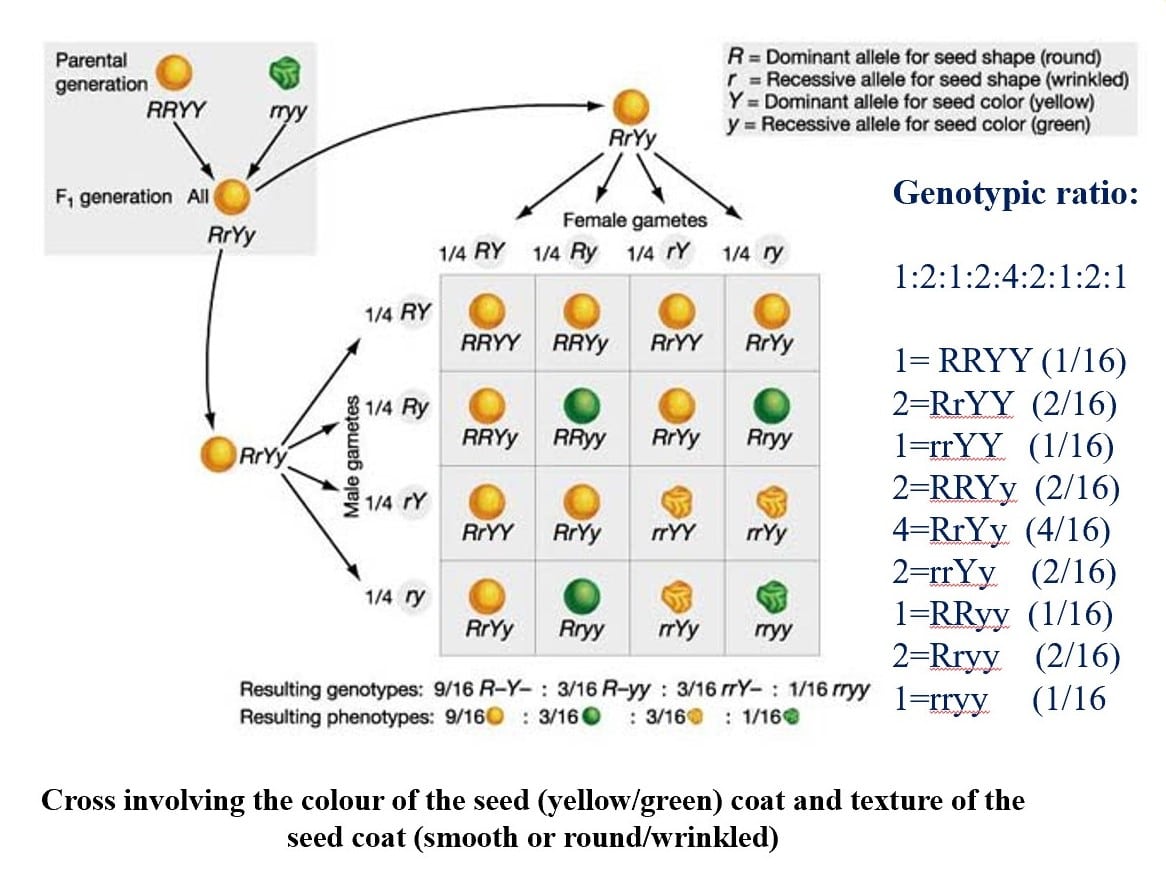
Mendel also performed experiments with plants that differed in two traits. He crossed plants that produced yellow, round seeds with plants that produced green, wrinkled seeds. The purpose of the experiments was to see if the two seed traits, color and texture, were inherited independently.
- Dihybrid Cross: Mating that involves parents that differ in two genes (two independent traits).
- The alleles of different genes segregate, or as we sometimes say, assort, independently of each other.
- This principle is another rule of genetic transmission, based.
BASED ON THESE RESULTS, MENDEL POSTULATED – Genes get shuffled – these many combinations are one of the advantages of sexual reproduction.
Fill Up the Form To Download Complete UNIT 8 A, B & C notes + Flowchart for Types of Cross
PROBABILITY
A probability is the ratio of the number of times a particular event is expected to occur to the number of trials during which the event could have happened.
P=a/n
Probability (P)
Number of favorable cases (a)
Total number of possible cases (n)
Probabilities and the laws of chance are involved in the transmission of genes.
PROBABILITY RULES
- Product rule
- Sum Rule
- Binomial Theorem
Contd…….
Fill Up the Form To Download Complete UNIT 8 A, B & C notes + Flowchart for Types of Cross
Download CSIR NET Notes PDF
- UNIT 1(A) Notes – Structure of Atoms, Molecules & Chemical Bonds – https://btnk.org/unit1a
- UNIT 1(B) Composition, Structure & Function of Biomolecules – https://btnk.org/unit1b
- UNIT 1(G) Ramachandran Plot – https://btnk.org/unit1g
- UNIT 2 Organization of Genes & Chromosomes – https://btnk.org/unit2
- UNIT 2D Cell Division & Cell Cycle – https://btnk.org/unit2d
- UNIT 3A – DNA Replication – https://btnk.org/unit3a
- UNIT 3B – RNA Synthesis – https://btnk.org/csir–notes-3B
- UNIT 5B : Gastrulation, Early Development In Amphibians – https://btnk.org/unit5-notes
- UNIT 6B : Plant Respiration – https://btnk.org/unit6-
respiration - UNIT 7B Notes Here – https://bit.ly/btnk-unit7B-
notes - UNIT 13 A Notes Here – https://bit.ly/btnk-unit-13A