CSIR NET UNIT 13 Immunotechniques Notes
UNIT 13 is an important unit for The CSIR NET life science exam. Though it’s very vast, it is scoring too. It deals with various techniques & their applications. Experiment-based questions can be expected from this unit that genuinely tests your research IQ & abilities. Some direct concept-based questions are often asked from the last four subunits.
REFERENCE BOOKS For CSIR NET UNIT 13
- Principles of Gene Manipulation and Genomics by Sandy B. Primrose, Richard Twyman
- Gene Cloning and DNA Analysis: An Introduction by T. A. Brown
- Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual by Joseph Sambrook, David Russell
- Fundamentals of Biostatistics by V.B. Rastogi
- Principles and Techniques of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology by Wilson/Walker
CSIR NET UNIT 13 Immunotechniques Notes
Techniques Covered
- Radioimmunoassay (RIA)
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA
- Western Blot
- Immunoprecipitation
- Immunofluorescence
- Flow Cytometry
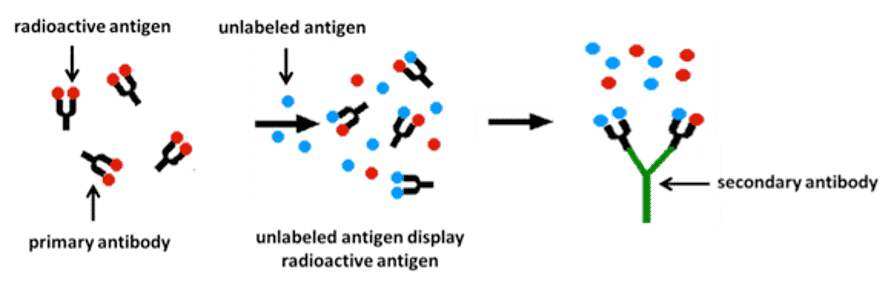
RADIOIMMUNOASSAY
- Developed by: Rosalyn Yalow & Solomon Berson
- For detection of insulin in human blood
- Very sensitive & specific assay
- Use antibodies to detect & quantitate antigens (analyte) in vitro
- Detects as low as a few picograms of analyte
- Analyte (Eg: Antigen) competes with radiolabeled antigen
- For binding to a fixed antibody
- Binding of unlabeled antigen to fixed & limiting amount of Ab
- Causes displacement of radiolabeled antigen
- Results in decreasing radioactivity of Ag-Ab complex
Practice Question
Q. Radioimmunoassay (RIA) can be employed to detect insulin in blood plasma. For this, 125I-labelled insulin is mixed and allowed to bind with a known concentration of anti-insulin antibody. A known volume of patients’ blood plasma is then added to the conjugate and allowed to compete with the antigen binding sites of the antibody. The bound antigen is then separated from unbound ones, and the radioactivity of the free antigen is then measured by a gamma counter. Following are some of the statements made about this assay:
(i) The ratio of radioactive count for the unbound antigen to the bound one is more at the end of the reaction.
(ii) The ratio of radioactive count for the unbound antigen to the bound one is less at the end of the reaction.
(iii) For a diabetic patient, the radioactive count for free antigen is less than that for a normal individual.
(iv) For a diabetic patient, the radioactive count for free antigen is more than that for a normal individual.
Which of the above statements are true?
(i) and (iii)
(i) and (iv)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
Answer: 1
Explanation:
- Classically, to perform a radioimmunoassay, a known quantity of an antigen is made radioactive and mixed with a known amount of antibody for that antigen, and as a result, the two specifically bind to one another.
- Then, a serum sample from a patient containing an unknown quantity of that same antigen is added. This causes the unlabeled (or “cold”) antigen from the serum to compete with the radiolabeled antigen (“hot”) for antibody binding sites.
- As the “cold” antigen concentration increases, more of it binds to the antibody, displacing the radiolabeled variant and reducing the ratio of antibody-bound radiolabeled antigen to free radiolabeled antigen.
- The bound antigens are separated from the unbound ones, and the radioactivity of the free (unbound) antigen remaining in the supernatant is measured using a gamma counter. (Hence statement i)
- In a diabetic person, insulin deficiency and hence lesser displacement of the radiolabelled antigen. (Hence statement iii)
For more practice questions with answers + Explanations & detailed notes on the above topics Join RAFTAAR CSIR BATCH For super fast & efficient CSIR NET Revision. Starts on 19th July 2022. Call Biotecnika Experts @ 1800-1200-1818 For More details or chat with us here.
SECONDARY ANTIBODIES
- A secondary antibody aids in the detection, sorting or purification of target antigens by binding to the primary antibody, which directly binds to the target antigen.
- The advantage of indirect detection is increased sensitivity due to the signal amplification from multiple secondary antibodies binding to a single primary antibody.
- In addition, a given secondary antibody can be used with any primary antibody of the same type and host species, making it an infinitely more versatile reagent than individually labeled primary antibodies.
- Secondary antibodies are generated by immunizing a host animal with the antibody(s) from a different species. For example, anti-mouse secondary antibodies are raised by injecting mouse antibodies into an animal other than a mouse.
- Goat, donkey, and rabbit are the most commonly used host species for producing secondary antibodies, but other host species may also be used.
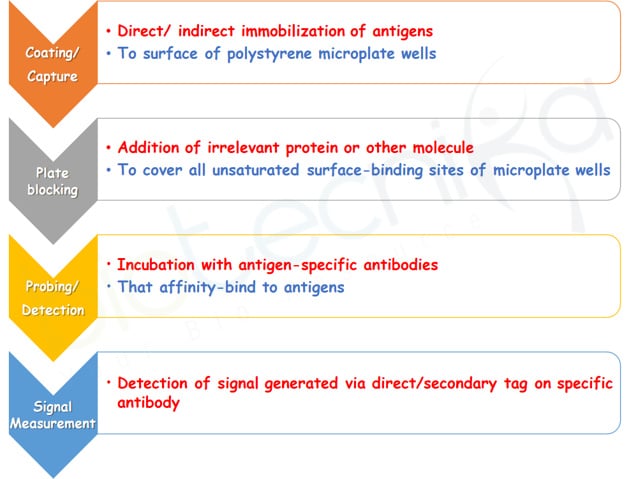
ENZYME-LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA)
WHAT IS ELISA?
- An Immunological Assay
- As described by: Engvall & Perlmann in 1971
Commonly used to measure
- Antibodies
- Antigens
- Proteins
- Glycoproteins in biological samples
- Diagnosis of HIV infection
- Pregnancy tests
- Measurement of cytokines/soluble receptors in cell supernatant/serum
BASIC STEPS:
- Carried out in 96 well/384-well polystyrene plates Allow multiple samples to be
measured in a single experiment.
Most Commonly Used Enzyme Labels
- Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)
- Alkaline phosphatase (AP)
- β-galactosidase
Other enzymes used: Acetylcholinesterase and Catalase.
FLOW CYTOMETRY NOTES CONTD…
Download UNIT 13B Immunotechniques Notes PDF
For more practice questions with answers + Explanations & detailed notes on the above topics Join RAFTAAR CSIR BATCH For super fast & efficient CSIR NET Revision. Starts on 19th July 2022. Call us @ 1800-1200-1818 For More details or chat with us here.
Wondering if Biotecnika has FREE Notes For CSIR? Check the links below for FREE CSIR Notes of other units.
Download CSIR NET Notes PDF
- UNIT 1(A) Notes – Structure of Atoms, Molecules & Chemical Bonds – https://btnk.org/unit1a
- UNIT 1(B) Composition, Structure & Function of Biomolecules – https://btnk.org/unit1b
- UNIT 1(G) Ramachandran Plot – https://btnk.org/unit1g
- UNIT 2 Organization of Genes & Chromosomes – https://btnk.org/unit2
- UNIT 2D Cell Division & Cell Cycle – https://btnk.org/unit2d
- UNIT 3A – DNA Replication – https://btnk.org/unit3a
- UNIT 3B – RNA Synthesis – https://btnk.org/csir–notes-3B
- UNIT 5B : Gastrulation, Early Development In Amphibians – https://btnk.org/unit5-notes
- UNIT 6B : Plant Respiration – https://btnk.org/unit6-
respiration - UNIT 7B Notes Here – https://bit.ly/btnk-unit7B-
notes - UNIT 13 A Notes Here – https://bit.ly/btnk-unit-13A
Download UNIT 13B Immunotechniques Notes PDF
Or
CSIR NET UNIT 13 B Immunotechniques Notes





























 measured in a single experiment.
measured in a single experiment.












