CSIR NET Life Science Notes – UNIT 2D Notes – Cell Division & Cell Cycle
CSIR NET UNIT 2 Part D – Cell division and cell cycle is a very important topic with respect to the CSIR NET Life science exam. One must never skip this topic as it’s not only important from the CSIR NET exam point of view but also clarity in concepts in this subject helps a lot in future research career too.
The CSIR NET exam is a highly competitive exam that requires a deep understanding of concepts related to cell division and the cell cycle. Here’s a guide on how to divide and study these concepts for the upcoming CSIR NET exam. Continue reading to download the notes & mind maps PDFs below:
Step 1: Understand the Basics of the Cell Cycle & Cell Division
Start by understanding the basic concepts of cell division and the cell cycle. This includes understanding the different phases of the cell cycle, the process of mitosis and meiosis, and the key regulatory mechanisms involved.
Step 2: Divide the Topics – Key Topics To Cover
Divide the topics into subtopics and create a study plan. Some of the key topics to cover include:
- The cell cycle: The different phases of the cell cycle, including interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
- Mitosis: The process of mitosis, including the different stages of mitosis, such as prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Meiosis: The process of meiosis, including the different stages of meiosis, such as prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, and prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II.
- Cell cycle regulation: The key regulatory mechanisms involved in the cell cycle, such as cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs).
- Chromosomes: The structure and function of chromosomes, including the role of centromeres and telomeres.
- DNA replication: The process of DNA replication, including the different stages of replication, such as initiation, elongation, and termination.
Download CSIR NET Cell Division & Cell Cycle Notes & Mind Maps FREE PDFs
Step 3: Use Visual Aids
Use visual aids such as diagrams, charts, and animations to help you understand and remember the concepts. Draw diagrams to illustrate the different stages of mitosis and meiosis, and use charts to compare and contrast the different phases of the cell cycle. We understand drafting & making all of this from scratch will take lot of time, thus Biotecnika to assist you and speed up your revision have prepared a set of CSIR NET Revision tools for your benefit – check them out below:
- KONCEPT Table For CSIR NET Life Science Exam
- Konceptika Lite – 100 Flowcharts on 100 Important topics of CSIR NET Exam
- CSIR NET Koncept Wheel Book
- Koncept Cloud – Latest Study Tool Revolutionizing CSIR NET Revisions
- Konceptika – The Flowchart Book
Important Video Lecture on CSIR NET UNIT 2 Cell Division & Cell Cycle
Step 4: Practice Questions & Revise Regularly
Practice questions are an essential part of exam preparation. Use practice questions to test your understanding of the concepts and identify areas where you need more practice. There are many resources available online for practice questions, including previous year question papers and online quizzes.
Download CSIR NET Cell Division & Cell Cycle Notes & Mind Maps FREE PDFs
Reference Books For CSIR NET UNIT 2D Cell Cycle & Cell Division:
- Cell & Molecular Biology: Concepts & experiments By Gerald Karp
- Molecular Biology of the cell By Alberts
- Molecular Cell Biology By Baltimore & lodish
CSIR NET Life Science Notes – UNIT 2D Notes
Cell Cycle
- The process of Generating Identical cells
- To produce a pair of genetically identical cells, DNA must be perfectly replicated and the resulting chromosomes must be segregated into two separate cells.
- Most cells must also double their mass and duplicate their cytoplasmic organelles. To accomplish these goals, a cell must go through the Cell Cycle.
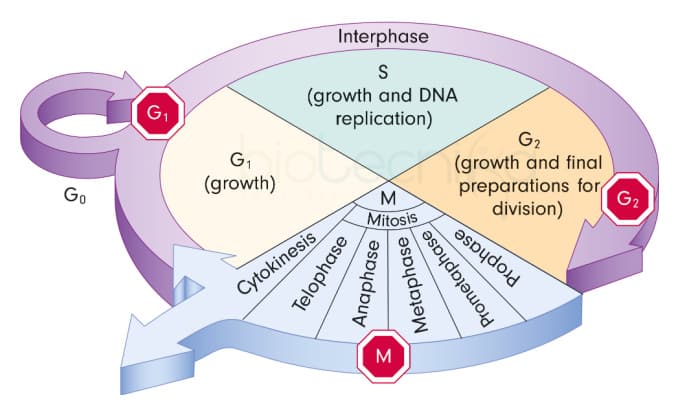
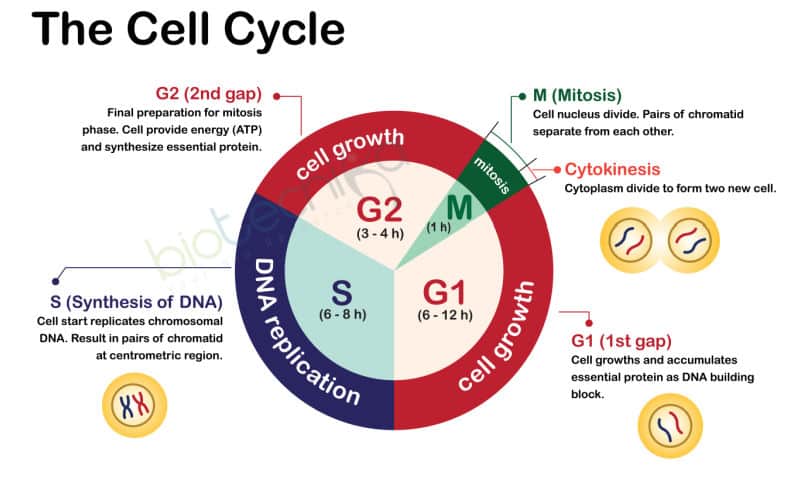
- Cell cycle – sequence of events by which cell duplicates
- Two main phases: M phase – mitosis, Interphase – time by which cell prepares for division by cell growth and DNA replication
- Interphase is divided into
- G1 –Gap 1- the period between the end of M and the start of DNA replication
- S phase- synthesis period
- G2- Gap 2- after DNA replication to initiation of M
Download Full PDF – CSIR NET UNIT 2D Life Science Notes – Cell Division & Cell Cycle
Interphase
- G1 – Cells undergo majority of growth
- S – Each chromosome replicates (synthesizes) to produce sister chromatids
Attached at centromere
Contains attachment site (kinetochore) - G2 – Assemble machinery for division such as centrioles
Length of each cycle
- 95% cell cycle – interphase
- M takes about 1h
- G1- 11h; S- 8h; G2- 4h M-1h
- S phase: DNA doubles
- No increase in the number of chromosomes
G1 Phase
- G1 is the period of time between the last mitotic division and the beginning of the synthesis of new DNA
- During G1, the cell surveys the environment and makes the decision to enter the cell cycle
- Proteins that promote cell division will be activated and force the cell towards the cell cycle
S phase
- The S phase, short for the synthesis phase, is a period in the cell cycle during interphase, between the G1 phase and the G2 phase.
- Following G1, the cell enters the S stage, when DNA synthesis or replication occurs.
- At the beginning of the S stage, each chromosome is composed of one coiled DNA double helix molecule, which is called a chromatid.
The enzyme DNA helicase splits the DNA double helix down the hydrogen bonds (the middle bonds). DNA polymerase follows, attaching a complementary base pair to the DNA strand, making two new semi-conservative strands. - At the end of this stage, each chromosome has two identical DNA double helix molecules
- During the S phase, the centrosome is also duplicated.
- The end result is the existence of duplicated genetic material in the cell, which will eventually be divided into two.
Download CSIR NET Cell Division & Cell Cycle Notes & Mind Maps FREE PDFs
G2 Phase
- The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs
- A phase within the interphase of the cell division cycle that prepares cells for mitosis
- Since the formation of new DNA is an energy-draining process, the cell undergoes a second growth and energy acquisition stage, the G2 phase.
- The energy acquired during G2 is used in cell division.
For Detailed Notes on Cell Cycle & Division, including Flow charts, Koncept Tables, Lecture Videos, QUestion Discussion, + Doubt Solving, Join Biotecnika’s CSIR NET + GATE Batch. Call Toll-FREE – 1800-1200-1818 For More details. or Email us @ [email protected] for scholarships.
Download CSIR NET Cell Division & Cell Cycle Notes & Mind Maps FREE PDFs































Thanks sir
Iam pursuing 12 th standard ISC n preparing for NEET. Planning to appear for bio Olympiad . Please share this material
Thank you
All classes