Paper-based sensors to detect Antimicrobial Resistance and relevant pollutants
A paper-based sensor that can detect antimicrobials or antibiotics that have an inhibitory impact on bacteria in water bodies by a see and tell mechanism has been developed by a team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Madras.
As the whole globe is undergoing the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, the scientists have actually cautioned that Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) could be the subsequent huge pandemic. This would entail a fight with several disease-causing microbes.
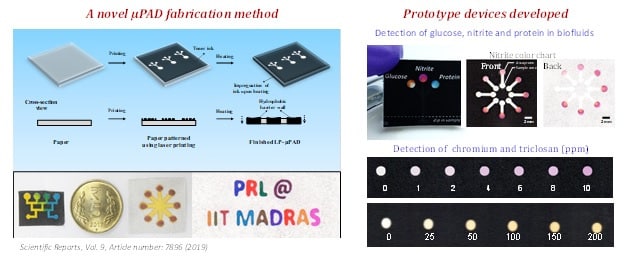
Water bodies are the main reservoir for the propagation and transfer of Antimicrobial Resistance. Routine tracking of antimicrobials, as well as antibiotic-resistant genes, is vital to analyze the present situation of Antimicrobial Resistance in India. In these situations, inexpensive and easy to use sensors to identify antimicrobials in water sources could be a practical device for environmental monitoring.
The new plan for cost-effective construction of the durable Laser Printed- Microfluidics Paper-Based Analytical Sensors crafted by the Indian Institute of Technology Madras Madras will aid in detecting antimicrobials quickly in the components per million scale. It will also help understand the relationship between Antimicrobial Resistance and Antimicrobial Resistance activating pollutants and help policymakers
in framing solutions to tackle the grand social Antimicrobial Resistance challenge.
The development of these paper-based sensors was backed by the DST, EPSRC under Indo UK Water Quality Research Program, and Government of India – Water technology Initiative in bilateral collaboration with the UK’s NERC. The new plan of merging adsorption-based pre-concentration utilizing reagents that undergo a determinable color variance enabled parts per billion level detection of antimicrobials. The procedure uses the easily available laser printer and thus provides a significant potential for a huge range of sensor construction. It can facilitate community-driven microfluidics as well as help with large scale monitoring.