How COVID-19 Testing Kits Work, What Tests Are Available?
COVID-19 testing is one of the key factors tackling the spread of novel coronavirus across the globe. For example, South Korea controlled the spread solely through mass testing by which they identified and isolated those with the disease. Testing is crucial to calculate the data necessary for making the right public safety measures like accurate infection and survival rates. During this coronavirus pandemic, many highly-priced, non-approved, or fake tests are offered to people for sale.
So what tests are being used by health officials, how do
they work and what developments are to come?What tests are available?
COVID-19 can be tested mainly in two ways. The first test looks for RNA of the virus using a technique called RT-PCR. This test can detect even a single virus particle in the swap collected from the nose or mouth of the patient.
The second test measures the antibody generated in blood serum in response to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Different types of antibodies are generated in the body in response to the viral components. Some are less useful, binding to some common parts of the virus without helping the defense mechanism.
How do the COVID-19 testing kits work?
RT-PCR Test
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction is a technique used to detect the presence of specific genetic material in the sample. To test Covid-19, the swab collected from the mouth or nose of the patient is treated with various chemical substances to remove substances like fats and protein and finally isolate RNA. The isolated RNA includes the patient’s genetic material and that of the virus.
The RNA is then reverse transcribed to DNA using specific enzymes. DNA fragments complementary to the viral genome is then added to this mixture of DNA. The DNA fragments will go bind to the viral genome if present. Later the mixture is placed in a RT-PCR machine where the target sections of viral DNA will get amplified ( identical copies generated). The marker added along with the mix will release fluorescence, which is measured by the computer. The computer will track the amount of fluorescence emitted, and when the amount goes over a certain level, the presence of the virus is confirmed.
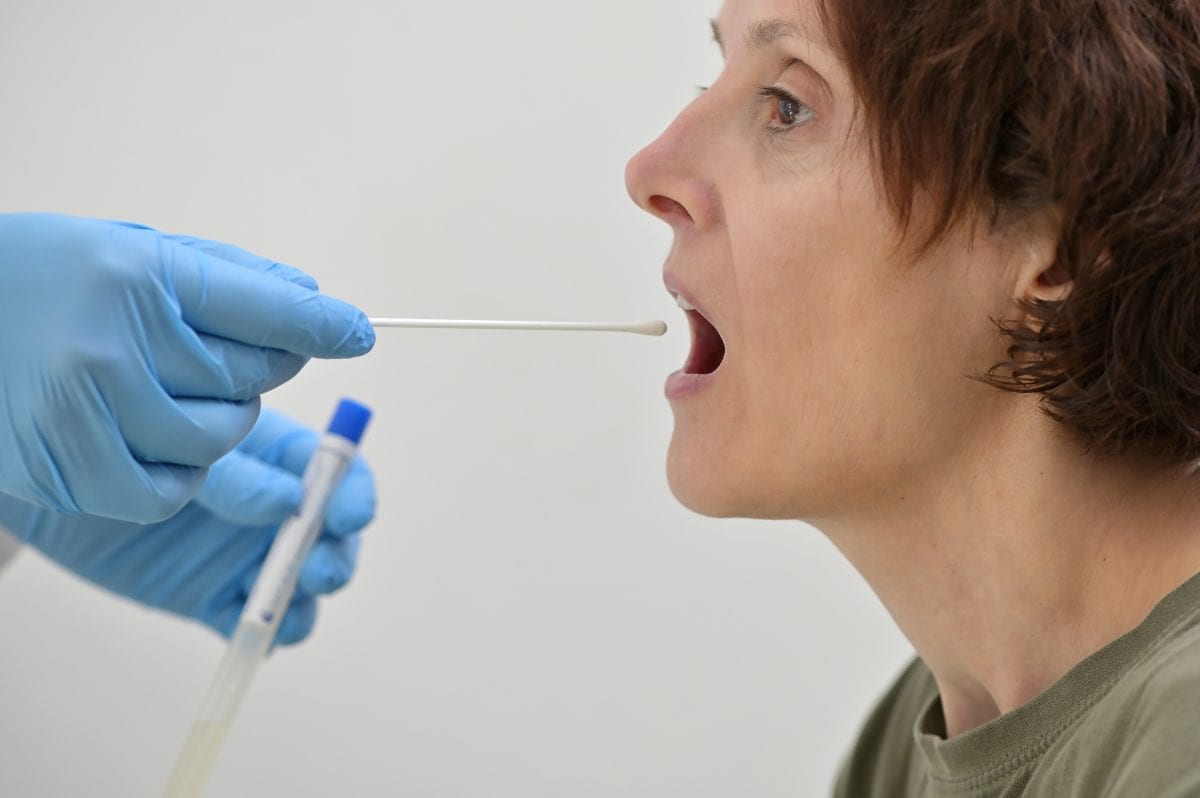
Antibody Test
This test is very simple. A small amount of blood sample collected from the patient is added to a test tube coated with virus “mash” or purified viral components. If the patient is infected and carries antibodies against the virus, they will get bound to the test tube. The test tube is later developed to see if any antibodies are present. If present, it confirms infection.
How good are current COVID-19 tests?
RT-PCR test is very sensitive and specific. However, the test cannot tell if one person was infected once he recovered from the infection as no viral particles are present in the body. The test needs a laboratory and takes time. It would take days to collect the sample, transport, process, and to generate results. Even the fastest cutting edge diagnostic technology, the rapid portable RT-PCR machines can take around 2 hours.
Antibodies generally take a few weeks to develop and last longer than the virus in the bloodstream. This test is very useful in providing a historical picture of the infections. The test can identify if a person was infected earlier, even after recovering from the disease. The test is used to diagnose the disease as well as to check if vaccines work.
However, the world health organization recommends the RT-PCR test as the current antibody tests for the novel coronavirus haven’t been fully tested to make sure they are reliable.
Recently the UK government announced that they would make 3.5 million home tests available in the country. But they need to make sure that the blood-based antibody testing is safe for use at home. Saliva-based antibody testing might be possible, but very less data is available for saliva than the blood serum.
Antibody Test Vs. RT-PCR Test
There are challenges in making and using antibody tests. The antibody test takes time to refine and needs viral components to be produced, purified, and standardized, unlike the RT-PCT test. Very carefully collected sets of patient samples are needed to check these tests are useful. The test needs to be checked with samples from different patients, because every individual produces a unique set of antibodies. Also, how long after the infection the sample test positive and how long it works after the recovery needs to be studied before these COVID-19 testing kits can be widely made available.
In contrast, RT-PCR detection can be assessed by taking a known amount of virus and checking the result. The virus has been grown in laboratories, and we have an accurate RT-PCR test for some time. The overburdened laboratories and labor requirements for running the test make it relatively slow and expensive.
Rapid Tests
The home testing antibody kits called rapid tests are cheaper and faster, but less accurate compared to the laboratory testing kits. They have a specially modified paper instead of a test tube where the blood flows and gives the “one line = negative, two lines = positive” stripes just like a home pregnancy test kit. These test kits need to be carefully designed and validated, which is why they are not widely used yet.
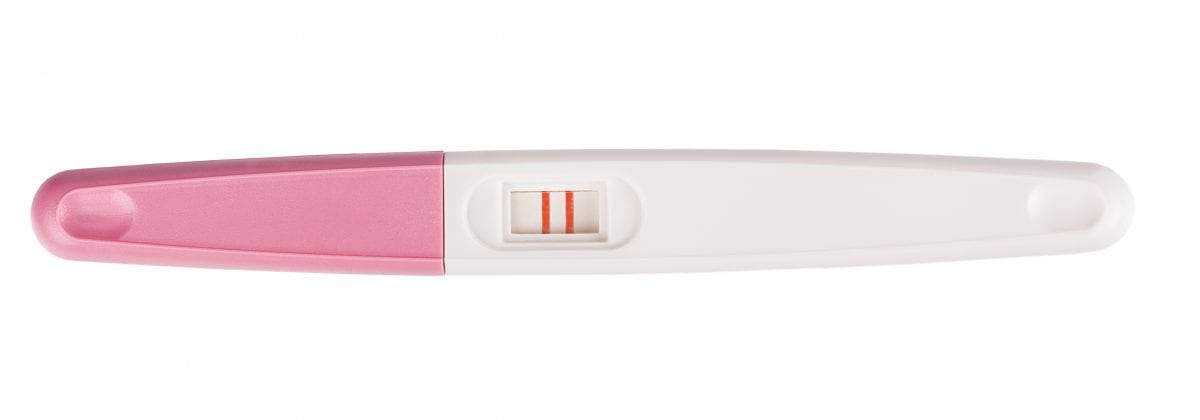
It is necessary that the tests are accurate and safe. Inaccurate tests can bring great damage during this current outbreak. Imagine you were infected, but still tested negative, you might go out and infect many more.
For some infections, you might test positive in an antibody test, even if you are not infected. This is because you have antibodies against something similar. And in the case of rapid tests, there is a chance that you read a negative result because the line is hard to see.
The accuracy of lab tests is far better than the rapid tests. Accuracy can be improved in a laboratory by combining multiple tests, for example, using lots of different viral fragments. But this needs more time, equipment, and expert interpretation.






























Very helpful God test kit are RTPCR
The best article. Very easy to understand. Thanks a lot Biotecnika!!