Marine Biologist as a Career – Marine Biology Career Paths
Table of Contents
How To Become A Marine Biologist?
Did you ever stand on the shore and wondered what treasure is hidden in the deep blue sea? Where are the waves coming from, and who are the neighbors of the jellyfishes or the shells? Did you ever have the urge to dive in and explore the depths? – if you have, then a Marine Biologist job is perfect for you.
The term “marine biologist” is applied in many disciplines and jobs in the marine sciences. Though many biologists study both which deal with the study of marine life, and also deal with the physical properties of the sea, Marine biology or Marine science is the study of the environment and all aspects of life in the sea. This includes marine animals, plants, and other organisms, including both vertebrate and invertebrate, in shallow seas, deep oceans, and the laboratory. The main aims of marine
biology are to understand the marine world better and to comprehend and predict changes in ecosystems affected by natural disturbances and human. So a marine biologist might be a biological technician, ichthyologist, microbiologist, systems analyst, fishery biologist, marine mammalogist, or a mathematician.Marine Biology Fields That You Can Choose
This is a broad-ranging career. You could go into academic research, fieldwork, laboratory work, consulting, outreach, or policymaking. You can choose from any of the following-
- Marine ecologist and dive operations manager
- Reef restoration project manager
- Marine biology technician
- Ocean Engineering
- Marine Archeology
- Marine Geology
- Aquatic Veterinarian
- Research Assistant
- Fishery data manager
- Environmental engineer
- Professor in marine ecology
- Postdoctoral fellow
- Oil spill response specialist
- Consultant in marine ecology
- Marine biotechnologist
- Scuba Diving Instructor and Underwater Filmmaker
- Marine policy expert
Although most roles require good research and scientific skills, specializing in a particular area, even a strong technical skill, is usually required for career progression – whether in coastal management, invertebrate biodiversity, fisheries biology, reef ecology, or marine pollution.
There are a number of marine science-related undergraduate and postgraduate degrees, but the key to having a successful career in these streams is by having relevant experience, either voluntary or paid. To prove your commitment and to develop your skillset, you need to be constantly on the lookout for opportunities and seize them at the right time as there is a lot of competition for jobs in this field.
Qualifications
To become a marine biologist, you’ll need to focus on a marine-oriented degree such as:
- Marine biology
- Marine biology and coastal ecology/oceanography
- Marine science
- Ocean and earth science
- Oceanography
You can enroll in programs like Bachelor of Science in Marine Biology, Master of Science in Marine Biology, Certificate courses in Marine Biology, Master of Philosophy (M.Phil.) in Marine Biology. Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Marine Biology according to your qualifications and eligibility.
If your undergraduate degree is a broader-based science degree, like botany, zoology or microbiology, you need to do postgraduate in the marine-related study.
Careers in marine biology are often research-based and, while it’s possible to study marine biology undergraduate degree and enroll in a semi-employed position on a conservation science project or go straight into volunteering, postgraduate study is required for better career prospects.
Postgraduate degrees range from Tropical coastal management to Masters in tropical marine biology and aquatic ecology and conservation. To have your career options open, studying more general science-based undergraduate degrees is suggested, after which you can specialize in your Master’s degree.
If you’re following an academic path in marine geochemistry or chemistry oceanography, ocean and earth science, and behavioral ecology, PhDs can be advantageous. Marine research organizations and universities conduct Ph.D. programs, and you may be able to undertake your studies on a part-time basis while working. The selection of a supervisor is essential. It’s better to select someone who is working in the specialist area that interests you.
Some of the Best Marine Biology colleges in India
Marine biology is an ever-evolving field, so continuous professional development in technical and practical skills, and relevant research is a vital part of the work. It also evidences your passion, commitment, and drive.
The colleges offering various courses related to Marine Biology:
- Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kerala
- Karnatak University, Karnataka
- Andhra Pradesh University, Waltair
- Annamalai University, TamilNadu
- Pondicherry University, TamilNadu
- Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, Surat
- National Institute of Oceanography, Panaji
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), Hyderabad
What Skills Do You Require?
Depending on your area of expertise, you will need to have different types of skills:
- If you are in fieldwork, then you should be comfortable in flexibility to work short-term contracts on varied projects with variable hours. You should be adaptable to live in basic living conditions in minimalist environments, to live-aboard research vessels, and to work in all types of weather.
- Have the capacity to work with a variety of people from government officials to local fisherman and to activists and professors
- whether working in an expedition team at sea or a part of a research team in a laboratory, you should have strong teamwork skills.
- Have high levels of physical fitness for fieldwork and experience in practical areas such as boat handling, scuba diving, and first aid
- a methodical and analytical mind for analyzing and interpreting data giving attention to detail for recording observations and accuracy in results
- if you’re working as a technician, then laboratory skills, such as sequencing, writing risk assessments, and standard operating procedures, strong numeracy, and IT skills is a must.
- If you are interested in teaching and supervising students for academic university roles, then strong communication skills are required for report writing and academic publications.
What Are Your Responsibilities?
Your duties as a marine biologist will depend on your area of work and could include:
- Conducting species inventories, monitoring and testing sea creatures exposed to pollutants
- Collecting and analyzing samples and data-using processes such as coring techniques, geographic information systems (GIS), visual recording and sampling
- Collecting and preserving specimens of unknown species and diseases and ranges or movements of marine population and mapping their distribution.
- Carrying out environmental impact assessments evaluating the likely environmental impacts of a proposed project or development, including socio-economic, cultural and human-health impacts
- Interviewing fishermen, stakeholders, and local divers, about animal behavior and local marine practices
- Lecturing on policy, planning, and management of aquatic activities
- Conducting expeditions on fishing and research vessels in polar, temperate and tropical seas
- Scuba diving to survey endangered organisms and implementing preservation strategies
- Designing scientific experiments and collating findings
- Conducting educational and awareness-raising work by presenting talks to the public, fellow academics, and commercial employers and government ministers.
- Senior-level management of new and existing projects within or outside an academic environment like preparing detailed reports for funders, commercial organizations, agencies, governmental bodies such as the oil companies drilling on the seabed.
- To help improve the ways in which we look after our oceans we need to communicate the latest advances in marine science through academic conferences, publications or outreach.
- The scientific information necessary to manage the marine environment best needs to be provided to policymakers and need to advocate this in the policy process through government liaison, press, and media.
What kind of Work experience do you require?
It’s essential to get some work experience to stand out from the competition. If you’re interested in a career in research, then approach your university supervisors, professors, or Ph.D. students who are working on some projects and ask if you can assist them in that why you will get some hands-on experience.
You could also volunteer as a research assistant to a specialist, attend conferences, present papers.
Send applications to organizations that interest you, such as museums or environmental consultancies or aquariums. This will help you build up a range of skills and understand what you enjoy before specializing.
In terms of fieldwork, consider volunteering for marine conservation organizations, local charities, local wildlife trusts, ocean clean-up organizations and sanctuaries and rescue centers (this includes paid-for experiences across the world).
Marine Biology Job Aspects
Marine scientists are employed by universities, international organizations, marine research institutes, government agencies, commercial companies, and not-for-profit organizations.
Examples include:
- Marine biologists have a chance to work as a scientist in Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute & Central Institute of Brackishwater Aquaculture in its various research centers along the coast of India. There are many academic institutions that teach the subject as well as carry out research in this vast field.
Jobs may be advertised on marine institute websites and universities, as well as on the websites of major companies. Career opportunities are also available in Oil India, the government sectors like the Meteorological Survey of India, Department of Oceanography, Geological Survey of India, etc.
What can you expect from this job?
You can always choose a fieldwork-based career or a lab or classroom-based career.
- University work is usually office and lab-based, although you might get plenty of opportunities for short or long-term expeditions abroad, like, If you are interested in dolphins or other marine mammals, research programs do exist in UC Santa Cruz and the University of Hawaii. The study of marine mammalogy and fish has many disciplines: anatomy and physiology, ethology (behavior), taxonomy and systematics (the study of their classification and evolution), natural history (the study of how a species lives) and ecology (how they interact with their environment). Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego, and some other universities, may not have specific programs on marine mammals, but they do have graduate students doing marine mammal-related research.
- Fieldwork can be laborious. You might be diving for several hours a day or working at sea in challenging weather conditions.
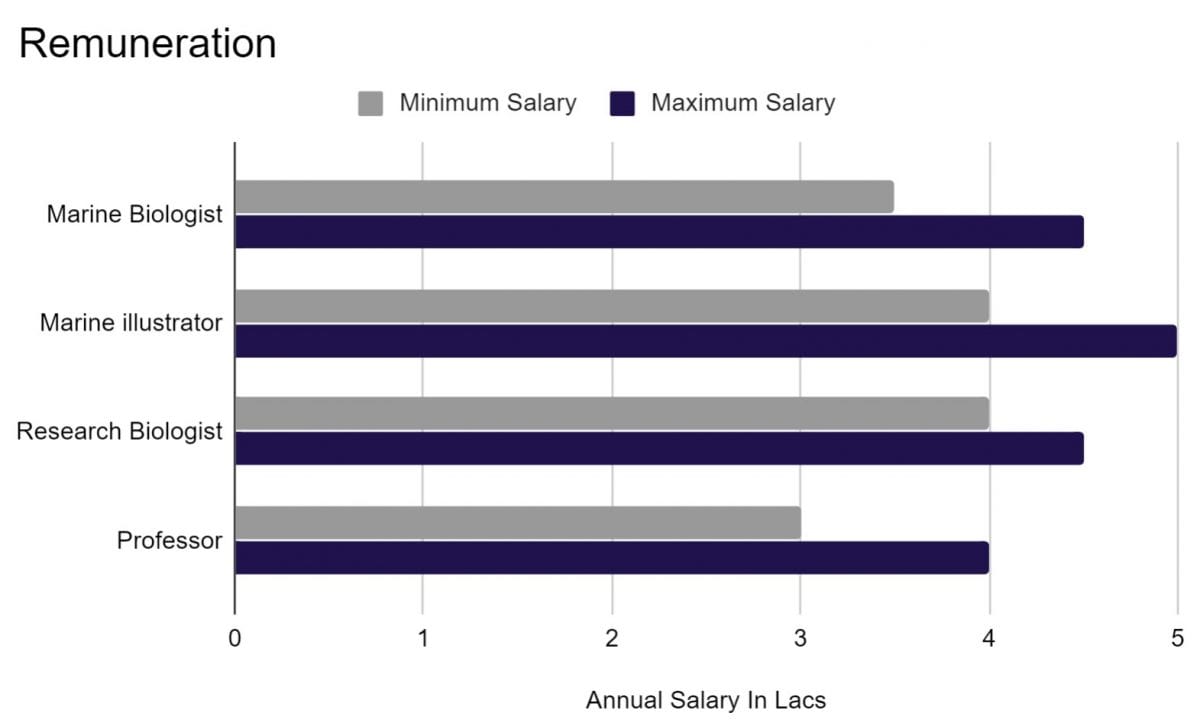
Remuneration for Marine biologists:
The salary level of Marine Biologists can vary greatly depending on a wide variety of factors, such as their level of education and experience, where they work, and many other factors. Their salary level can also depend on whether they are employed by a government agency, private-sector organization, or a non-profit organization. A marine biologist working with smaller institutions earn less than those working in elite research institutions.
- The salary is relatively higher in the private sector.
- An entry-level marine biologist (1-3 years of experience) earns an average salary of ₹5,07,061. On the other end, a senior level marine biologist (8+ years of experience) earns an average salary of ₹8,78,858.
- At the start, one can earn between Rs 12,000 – Rs 20,000 in the public sector, depending on the organization, a marine biologist can earn up to Rs. 35,000 to Rs. 45,000 per month in an Indian Organization and around Rs. 75,000 to Rs. 1,00,000 in a foreign organization.
- The salary of Marine biologists is comparatively higher in foreign countries.
Upcoming Avenues in the Field of Marine Biology
Marine biotechnology research is one of the emerging specializations which is applicable in many areas. The biomedical field associated with research to develop drugs from marine organisms, and Molecular Biology where research is based on marine organisms- from microscopic bacteria, plants, and animals to marine mammals- to detect their exposure to pollutants, diseases, and the source of contaminants affecting them, come under this field. Marine biotechnology research uses the latest breakthroughs in modern molecular biology, cell science and genetic engineering to solve basic problems in marine resource biology; to improve the production of chemical, food, energy resources and medical, from the ocean; and to develop new products and industries based on more efficient use of the ocean’s resources.
Marine Biology, one of the most all-encompassing fields of Oceanography which deals with the study of life in the ocean and all of its biological manifestations. Marine biology relates to all marine organisms, from small plankton to giant whales.
So all the marine enthusiasts out there, you can definitely think of taking up this exciting field as your career.
Editor’s Note: Marine Biologist as a Career, Marine Biology Career Paths, How To Become A Marine Biologist, Marine Biologist as a Career, Marine Biology Career Paths, Marine Biologist as a Career, Marine Biology Career Paths, Marine Biologist as a Career, Marine Biology Career Paths, Marine Biologist as a Career, Marine Biology Career Paths.
 is a senior – experienced faculty at BioTecNika. She has a specialization in botany, cell biology, and plant tissue culture. Being one of the most popular educators at Biotecnika, she keeps her students updated with the latest developments in the field of science. She also has a keen interest in the field of Biodiversity.
is a senior – experienced faculty at BioTecNika. She has a specialization in botany, cell biology, and plant tissue culture. Being one of the most popular educators at Biotecnika, she keeps her students updated with the latest developments in the field of science. She also has a keen interest in the field of Biodiversity. Co-Author: Prathibha HC