Life Sciences – Definition, Branches, Examples & Importance in Today’s World
Welcome to the world of Life Sciences!
From the spectacular discovery of the double helix (DNA) in the 20th century to the advanced and transformative application of Gene Editing, Genomics, Bioinformatics, and Artificial Intelligence in the 21st century, Life Sciences has become the keystone of human progress.
It is the field of questioning and understanding everything present on this earth, from complex, massive ecosystems sustaining life on our planet to the tiny, microscopic Bacteria in our gut and soil.
Life Sciences is far more than Academic curiosity and knowledge; it drives Technological innovation, Healthcare innovation, Economic growth, and Environmental Sustainability worldwide.
Living organisms surround us in numerous ways we barely even notice, like the tiny Bacteria in the soil helping a seed sprout, or the cells dividing in your body right now as you read the article. Such a delicate and intricate balance of ecosystems keeps our planet livable and growing.
The profound and Scientific field dedicated to uncovering the underlying secrets of the living world is the only field of “Life Sciences.”
This is the field that has contributed to the Scientific world and society the most. Life Science has unlocked our Genetic Code, given us Vaccines and advanced therapeutics, and is now actively helping with global hunger and climate change.
In an advancing era defined by futuristic innovations in Biotechnology, global health, and Precision and Personalized Medicine, understanding what Life Sciences actually entail has never been more critical. It resides at the heart of innovation and advancement, answering humanity’s most important questions: How does life evolve, and how do we protect our Earth for future generations and sustain it? Or how do diseases truly arise? How can we fight Diseases and live a better and healthier life? Or how can we grow food sustainably for billions of years altogether?
Let’s understand this essential subject of Life Sciences, simply and clearly, and in a way that gives us an insight into why Life Science is one of the most impactful and exciting of all.
What Is The Life Sciences Field?
At its core, the Life science definition is the systematic study of living organisms and their vital processes. It is a field dedicated to understanding the mechanisms of every life, from its birth and growth to its interactions and adaptations with the environment and other beings.
Modern Life Sciences is structured around three primary interconnected tiers of Research that successfully transition knowledge and insights from pure Discovery to practical application, these are:
- The Discovery (Basic Science): This Scientific tier is driven by the fundamentals and curiosity, Biological information without a specific therapeutic intention. It gives us foundational knowledge.
- For Example, studying and understanding the signaling pathways in a simple organism, such as yeast, to understand universal cell cycle regulation.
- The Testing (Applied Science): This is the focused Scientific effort to utilize the basic Scientific knowledge and findings to address a targeted and specific problem, often involving testing theories in pre-clinical (non-human) environments.
- For Example, exploring the mechanism by which a newly identified viral strain infects cells, leading the way for a potential drug target.
- The Bridge (Translational Research): This is the significant step that converts Reserach laboratory Science into real-world solutions for public benefit as well as human health. It is the “bench-to-bedside” journey, which includes human Clinical Trials as well.
- For Example, A promising drug compound developed in the laboratory through Clinical Trials to gain approval from the Regulatory authorities as a drug therapy for a type of Cancer disease.
This self-reinforcing and continuous cycle of Scientific developments ensures that our theoretical knowledge is executed at the laboratory level and further benefits society and the living.
The Branches of Life Sciences
Our planet Earth is quite rich and varied in all forms, and Life Sciences is divided into specialized fields, yet deeply interdependent, such as:
-
The Core Functions and Organisms
- Biology: The Major field that explores the fundamental and core principles of life, function, habitat, adaptations, lifestyle, as well as growth.
- Biochemistry: This field merges the fundamentals of Biology along with Chemistry to decode the complicated Chemical reactions (such as metabolism and Biological pathways) that keep every living cell “alive”.
- Microbiology: This field explores and understands the microorganisms, viruses, fungi, as well as Bacteria, that shape our environment and health.
- Zoology & Botany: These fields are the systematic study of animals (Zoogoly) and plants (Botany), providing knowledge and insights essential for food security and conservation.
- Immunology: This field studies the immune system of our body, the body’s defense against any diseases or infections, which is essential to understand for Cancer therapy and vaccine or therapeutic development.
- Physiology: This subject explores how tissues, organs, and organ systems function in living beings, which is vital for understanding health and disease states.
- Molecular Biology & Cell Biology: Explores the most minor functional and structural units of life as well as their molecular machinery. These two subjects provide foundational knowledge for Cancer Biology, Drug Discovery, as well as Regenerative Medicine.
-
The Modern Information Fields
- Bioinformatics: The application of Statistics, Computer Sciences, and Biology to analyze, manage, as well as interpret the explosion of massive Biological datasets.
- Proteomics: The large-scale study of proteins as well as their intricate structures, which are the major functional workers of the cell in our body.
- Genomics: Explores the entire Genome (set of genes) and how it interacts with itself and the environment.
- Genetics: Focuses on DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), Genes, as well as heredity, the molecular blueprint or a life manual of lifeforms.
- Pharmaceutical Science: This field covers drug development, drug design, drug testing, as well as the Regulatory pathways (both local and International) to bring new therapeutics and medications to patients effectively and safely.
-
Applied and Environmental Science
- Biotechnology: This major field applies principles from Biological Sciences and Engineering. It is a field that manipulates Biological systems (living organisms as well as their products and byproducts) to develop Technology and products or compounds, from developing mRNA vaccines to producing beer.
- Neuroscience: This field is dedicated solely to the nervous system, the brain, and their behavior, advancing our understanding of neural function and the treatment of Neurological diseases and disorders.
- Ecology: This field deals with how living organisms interact with one another as their surroundings and environment, providing the guiding principles for Climate and Environmental Science as well as Biodiversity conservation.
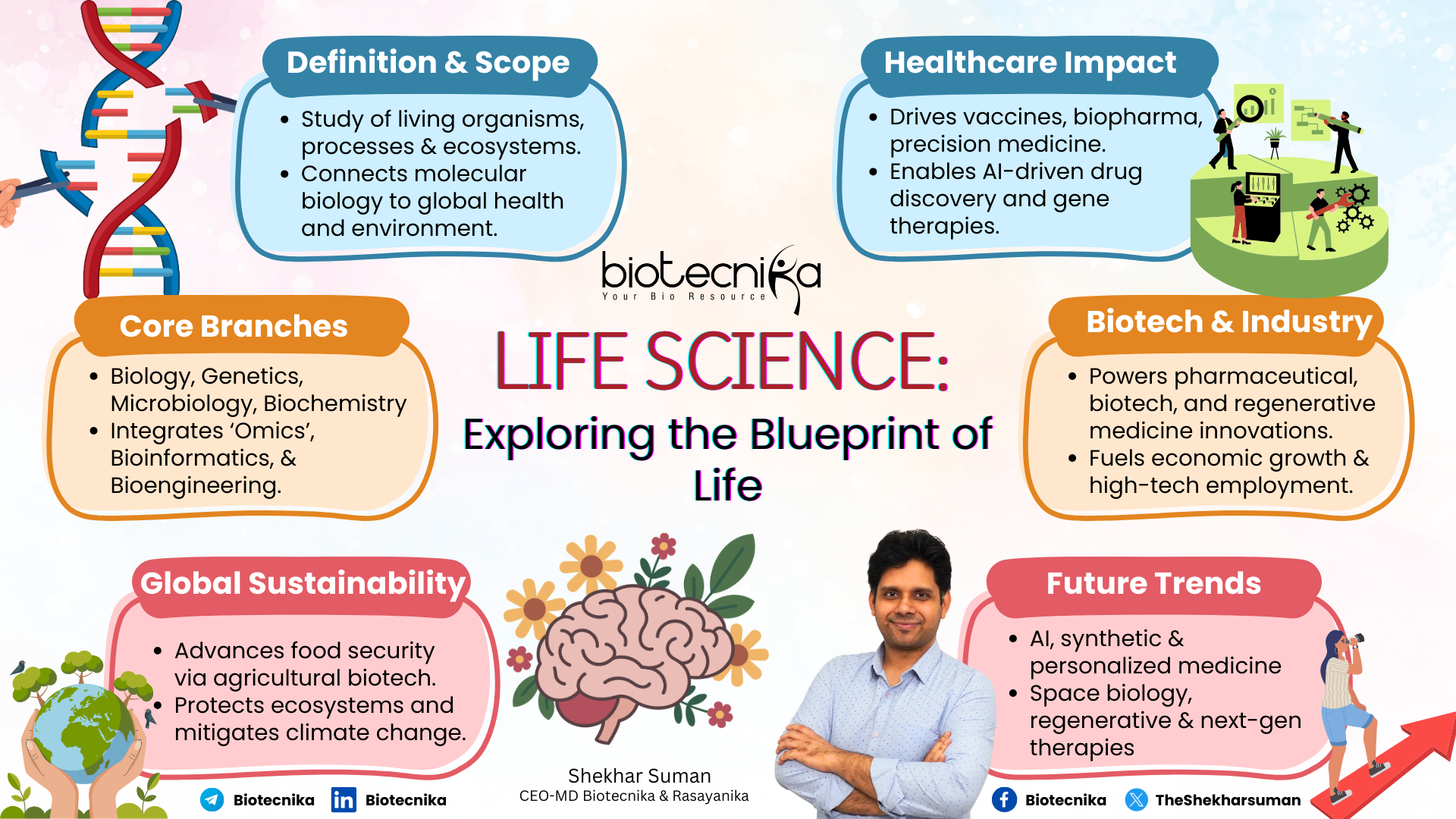
Why Do These Matter Today & In The Future?
Life Science is not just an Academic field; it is the most influential factor driving human potential, global security, and economic growth.
-
Transforming Healthcare
Life Science is the engine behind every significant Medical or Environmental advancement. It allows us to:
- Power the global Biopharmaceutical Industry, which works tirelessly. There is an integral partnership with AMCs (Academic Medical Centers) and specialized CROs (Contract Research Organizations). This combination accelerates and executes Clinical Trials to accelerate Drug development and the global market.
- Develop life-saving and targeted Drugs by analyzing diseases and disorders at the molecular level.
- Create personalized medicine by leveraging individual genetic data to tailor treatment plans.
-
Feeding a Growing World
As the global population rises, life Scientists are crucial for achieving food security and sustainability:
- They develop high-yield, disease-resistant crops through agricultural Biotechnology.
- They study the microbiome and soil Biology to reduce the environmental footprint of farming and optimize nutrient use.
- They provide the most comprehensive knowledge required for sustainable animal husbandry.
-
Protecting the Planet
Environmental Science and Ecology provide the indispensable framework for addressing our most severe global challenges:
- Informing global climate policy by modeling how ecosystems respond to Environmental and atmospheric changes.
- Developing Bioremediation solutions, using natural processes to clear up pollution (such as water, air, and land).
- Guiding Environmental conservation efforts to maintain biodiversity and protect species.
The global economic footprint of the Life Sciences industry, which is measured in the trillions, highlights its role as a dominant force of stable and required Scientific innovation.
The Role of Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
The Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology industries are among the fastest-growing sectors within the vast field of Life Sciences. They bridge applied innovation along with the foundational Research and Development.
- Biotechnology companies develop therapeutic proteins, diagnostics, Genetic tools, engineered organisms, as well as vaccines.
- Pharmaceutical companies, on the other hand, focus on Drug Development R&D (Research & Development), Regulatory approval, large-scale manufacturing, as well as Clinical Trials.
Both industries depend on all aspects and fields of Life Sciences, but majorly on:
- Cell engineering
- Genomics
- Regulatory science
- Bioprocess
- Clinical Science & Research
- AI-driven analytics
Their convergence is reshaping how medicines are discovered and delivered worldwide.
Life Science is way more than a collection of fields; it’s a living testament to human ingenuity and curiosity. The advancing convergence of Biology with AI, Engineering, and Data Science means that the rate of innovation is evolving exponentially.
Innovations such as Gene Editing and AI-designed Medications (which predict novel molecular structures) are redefining Medicine and Science.
As we progress into a Technologically evolving era of Biology, understanding Life Sciences is key to participating in the future.
For Life Sciences students and professionals, this field offers endless career opportunities across roles ranging from Regulatory Affairs and Bioinformatics to Clinical Research and R&D.
Ultimately, understanding life and lifeforms is not just for Academic scores; it is the most powerful tool we have for securing and improving our future, as well as that of Mother Earth. If you want a career that truly makes a difference, then Life Sciences is where the technologically advancing future is being built.
In essence, Life Sciences is the blueprint of life itself, a discipline defined by curiosity, sustained by knowledge, and driven by the desire to make the world better for all living beings.