AI and Robotics in Biotech Jobs
AI and Robotics are no longer just fancy terms; they are the present that’s reshaping the future. AI and Robotics have become an integral part of our daily activities, regardless of the field of interest. From Biotech to Healthcare, it has successfully entered the pipeline across AI-driven drug discovery, robotic sample handling, automated QC lines, molecule/ reaction prediction, and data retrieval. There is a profound shift across diagnostic labs, biotechnology companies, hospitals, CROs, and manufacturing plants. All these happened overnight? Definitely not. Over the past five years, there has been a precise nudge towards AI, robotics, automation, and the gradual integration of them in healthcare, bridging the gap between life science and machines.
It is very obvious to think if AI and Robotics can replace the work humans do? The threat of losing our jobs is common, but the reality is very different from what we imagine. As of what’s unfolding now, AI and automation can not replace humans, but redesign and reinvent the already existing jobs, making the workflow rapid and accurate. Along with the top companies in biotech, pharma, and healthcare, several startups have come up with amazing inventions that reshape the biological world.
The Acceleration of AI and Robotics in Indian Biotechnology?
India is one of the technology-driven Biotech hotspots. Three parallel developments have made this possible.
- India’s extension as a global manufacturing partner in vaccines, biosimilars, etc. indicates that companies are upgrading their workflow with AI and automation. As a result, there’s a massive rise in clinical research and manufacturing.
- The demand for more talent in computational biology and bioinformatics is going up. Even the pharma companies openly acknowledge the need for convergence of computational skills and biology.
- Programs like BIRAC, Make in India, and Digital Health push companies for modern infrastructure and technologies, and upgradation becomes a natural solution.
How AI is transforming Biotech Roles in India
- Pre-Research and Drug Discovery: Traditionally, researchers used methods like manual experiments, combinatorial chemistry, and assay setups to identify the right combination of drugs. AI in Drug Discovery has almost replaced many bench pipelines. AI models can now determine the lead molecule, and Machine learning models can predict drug-target interactions, along with suggesting molecules. Algorithms can optimise protein sequences and predict experimental priorities.
Examples:
a) Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) is building AI platforms that help in in silico drug discovery
b) To interpret Complex genomic datasets, MedGenome is using Machine learning
This doesn’t mean the wet labs are disappearing. Instead, the researchers will spend time in analysing the data quality, optimizing workflows, and results interpretation.
- Hospitals and Diagnostics: Major Hospital Brands like Apollo, Manipal, and Max Healthcare are moving towards AI systems for Analysis of pathology slides, genome sequence interpretation, and automated clinical decision support.
- Bioprocess and Biomanufacturing: Companies like Syngene, Serum Institute, and Dr. Reddy’s are already integrating AI and automation into bioprocesses, particularly in vaccine, insulin, and biosimilar production, as well as fermentation. AI is being used in sensor-driven formulations, fermentation monitoring, and yield optimization.
- Clinical Research Organization(CROs): India’s CRO sector (IQVIA, Aragen, Synegen, Veeda, and Novotech India) is evolving rapidly due to the integration of AI in data cleaning, clinical trial management, biomarker analysis, etc.
The use of AI isn’t taking away jobs but redefining the already existing roles to an advanced level, reducing the burden on humans, and making the workflow more efficient.
Robotics in Wet Labs and Manufacturing
Biotechnology has many routine and repetitive tasks, from pipetting, plating, labelling, and running standard assays to documentation, regulatory reports, and monitoring bioreactors. This job is made easy by robotics. These tasks are monotonous and prone to human error, but with robotics, the work rate and accuracy have been improved. Colony pickers are faster than humans. Syngene uses automation for peptide synthesis and DMPK workflows; IISc and IIT labs use robotic handlers for genomics research. Robots now execute sterile filling, label inspection, and packaging in bioreactor plants. Automated guided vehicles are used for material movement. Robotics in biotech is not restricted to manufacturing; diagnostic labs now use robotic sample sorters, automated analyzers, and AI-based imaging systems that reduce turnaround time from days to hours.
Benefits of AI and Robotics in Biotechnology and Life Sciences
- Reduction in Repetitive Work – Automation handles the routine tasks, while the researchers focus on data analysis and interpretation.
- With automation, productivity has increased drastically, and outputs are well defined.
- Betterment of accuracy in the fields of diagnostics, manufacturing, and genomics, and reduced human error.
- Emerging career paths – From lab to laptop, computational biology to AI and Robotics, the Biotech ecosystem is expanding, creating more career opportunities.
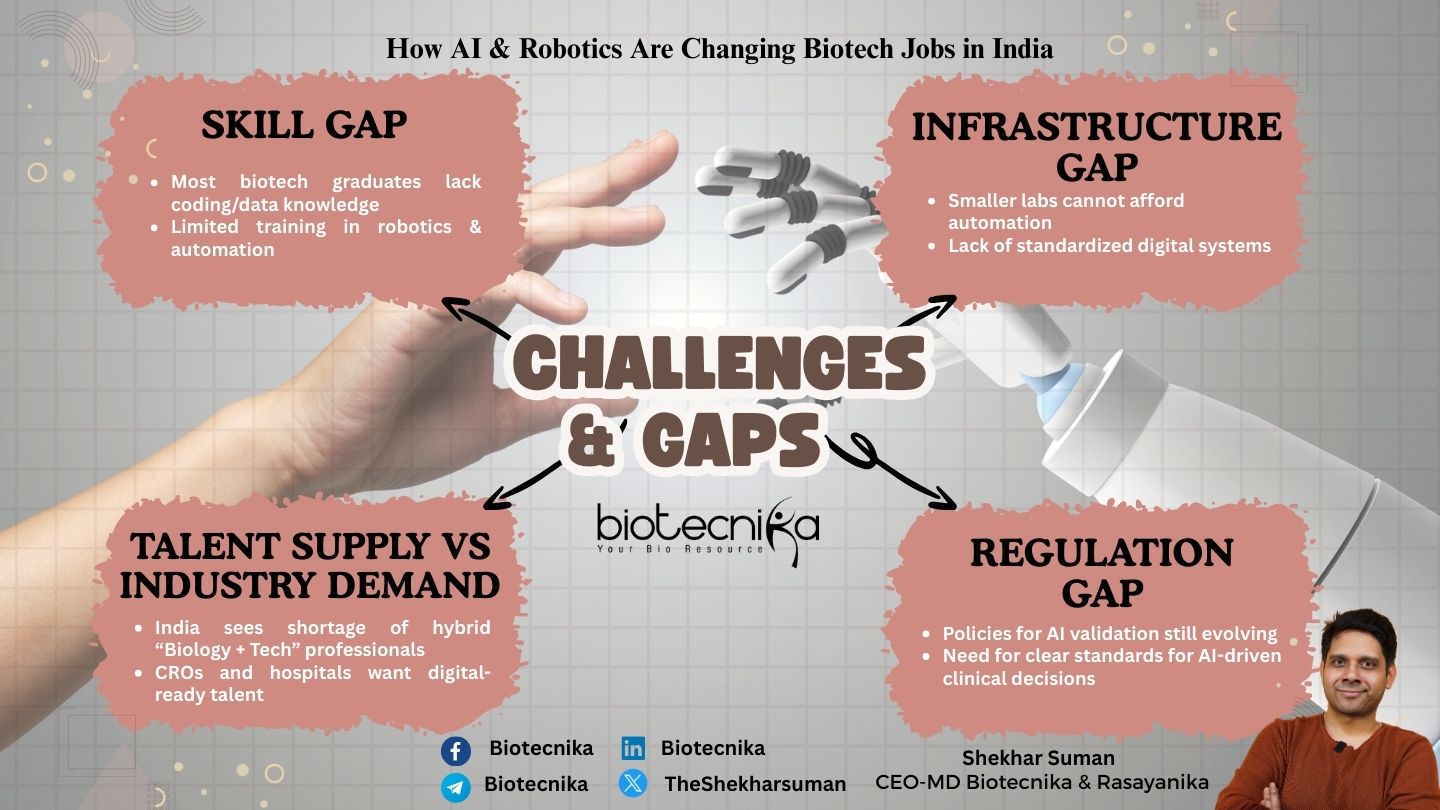
The Gaps and Challenges Specific to India
Despite these advancements in the Biotechnology field, India still struggles to build a biotech workforce ready for AI and robotics.
Certain challenges slow down India’s progress:
-
- Curriculum Mismatch: Most educational programs still teach outdated techniques and fail to focus on the rising areas such as automation principles, computational biology, AI basics, and lab robotics. Students/freshers who are well-versed in theoretical knowledge lack practical exposure to modern advancements. Often, fresh graduates enter the industry unprepared, while the industry quickly moves forward with emerging trends.
- Shortage of Automation-Literate Biologists: Companies usually hire such candidates who are proficient in both Biology and technology, but constantly struggle to find an effective one. Universities teach wet lab skills and private institutes focus on data science; students ultimately need both skills.
- Limited access to High End Robotics – Economic Constraints: At present, only a few companies in Tier 1 cities can afford advanced robots. Small labs and academic institutions still use traditional techniques and lag behind.
- Regulatory Frameworks: The global literature focuses on the FDA and EMA guidelines, the Indian NABL, ICMR, DCGI, and CDSCO have not yet published structured frameworks for AI and Robotics in Biotechnology equivalent to US/EU guidelines. Detailed regulatory guidelines are needed for AI-based diagnostic tools, automated decision support, Robotics in GMP environments, Validation of AI/ML models in manufacturing, and drug design.
- Fewer Training Programs: Unlike AI, robotics requires hands-on training, which India lacks. Lab Automation courses and GMP automation training institutes must be implemented within the life sciences.
This gap, however, presents an opportunity. Professionals who learn digital skills even at a basic level, do internships, and undergo training will immediately stand out. Learning to operate and code with Python and computational skills will be in greater demand in industries. The future belongs to those who embrace this blended identity: part biologist, part data interpreter, part digital operator.
New Biotechnology Job Roles Emerging in India
AI-driven Roles
- BioAI scientist
- Clinical AI analyst
- Machine-learning engineer for drug discovery
- Biomedical data scientist
- Model validation specialist
Robotics-Driven Roles
- Lab automation specialist
- Industrial robotics technician (GMP)
- Automation validation engineer
- Digital QC/QA professional
- Manufacturing automation controller
Hybrid Roles
- Computational biologist with bioprocess knowledge
- Bioinformatics engineer with wet-lab experience
- Biotech product manager with AI/ML skills
- Regulatory professional for AI-enabled devices
What India Needs to Focus on?
To strengthen AI and Robotics in Biotech, India must address:
- Skill development by introducing automation models in the curriculum, developing lab robotics training institutes, expanding bioinformatics and AI certifications and training programs in Industries and CRO.
- Frame Regulatory guidelines for AI and Robotics usage in diagnostics and labs
- Academic and Industrial Integration that allows students to work on projects and get hands-on experience of the emerging AI and robotic models.
- The development of AI databases and infrastructure investments are essential for better research.
Are AI and Robotics replacing Humans?
AI and robotics are replacing humans’ tedious and repetitive work, but not the Human mind. AI can only identify the data patterns, screen enormous data, and automate predictable workflows. Ultimately, it is humans who must intervene and analyse the data, and interpret the results. AI, in addition, can only follow the command of a human and cannot design experiments, troubleshoot unexpected results, and make ethical decisions. The algorithm on which the automation is based requires human input to structure it. So the job descriptions are changing, the roles are getting redefined, but the jobs are not shrinking. It helps avoid repetitive tasks and makes the workflow more efficient and quicker.
Future Outlook – Humans and Technology Grow Together
AI and Robotics are no longer just a trend; they are becoming the part and parcel of modern research, diagnostics, clinical trials, and manufacturing operations. AI brings in pattern recognition and speed, while robotics extends to precision and efficiency. They are reshaping how scientists and researchers work without replacing them altogether.
The transformation of scientists from manual labour to automation, from repetition to deep thinking and innovations, from routine tasks to quality decision making, the evolution of Biotechnology is remarkable, although there are certain loopholes. The rise of automation in the Biotech and life science industry demands more skilled personnel in both the Biology and Computational domains.
These advancements have opened doors to new roles, creating employment opportunities. For students, researchers, and professionals, embrace the change and move ahead with the future of Biotechnology and Life Sciences. AI and Robotics are not our competitors but our supporters in building the future of Indian Biotechnology.





























