Role of Pharmacovigilance in Drug Safety
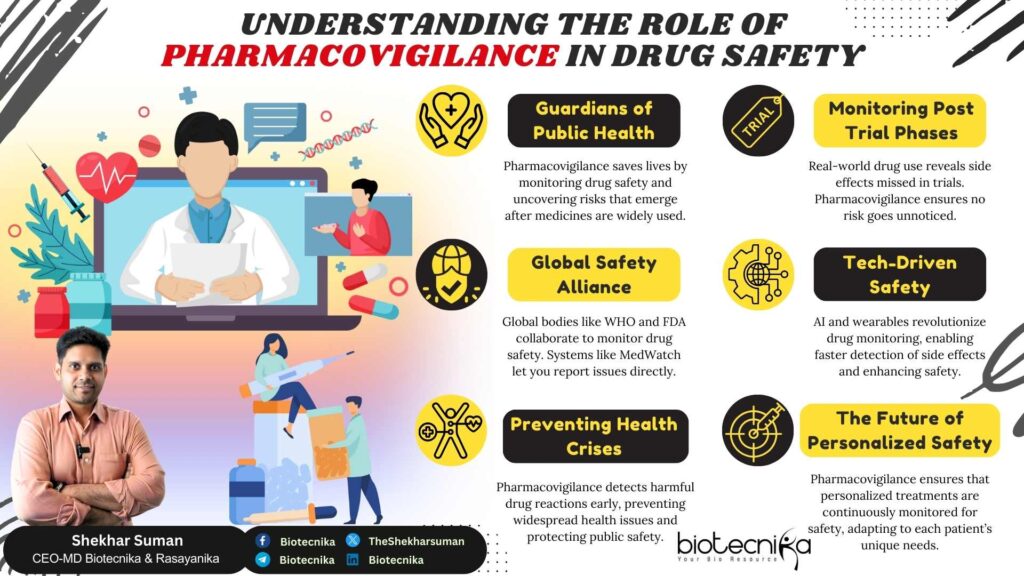
Do you have faith in the Global Healthcare system? Most of us believe that once a medicine reaches the market, it is completely safe. However, the harsh reality of drug safety doesn’t end with clinical trials. Clinical trials provide a glimpse into potential risks within the given population size and density. The broader and real-world experience often uncovers the full extent of their safety, efficacy, and dangers. By the time these risks come to the limelight, it’s usually too late for many people. At the core of this medication path lies Pharmacovigilance (PV), a crucial field that ensures the safety of medicines once they are launched in the global market.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Pharmacovigilance is “the Science and activities relating to the detection, assessment, understanding, and prevention of ADRs (Adverse Drug Reactions) or any other drug-related problems.” Pharmacovigilance plays an important role in safeguarding public health by ensuring that the medications used are effective, pure, and safe to use. The main aim of Pharmacovigilance is to ensure medicines’ effectiveness and safety. PV involves collection as well as analysis of data on the side effects of medications, identifying patterns, as well as assessing potential risks associated with their use.
Importance of Pharmacovigilance in Public Health
-
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs):
Pharmacovigilance’s one of the main roles is to understand and identify ADRs, which are unintended reactions with harmful effects resulting from the use of a medication. Through robust monitoring systems, PV ensures that potential risks associated with drugs are quickly identified and addressed. ADR identification is particularly essential during the early post-marketing phases when the drugs are exposed to a large population.
-
Developing & Implementing Safety Protocols
Pharmacovigilance professionals work diligently to develop and implement safety protocols that minimize the risk of medical reactions. They provide guidelines for Healthcare professionals on managing ADRs, training for PV professionals to handle safety-related situations, as well as strategies for prescribing medicines and treatments responsibly. PV professionals also provide risk-minimization measures, such as drug dosage adjustments, special monitoring for vulnerable and critical patients, and clear, detailed patient information leaflets.
-
Continuous Monitoring & Assessment
Pharmacovigilance involves continuously monitoring drugs throughout their development, production, and market lifecycle. Pre-market clinical trials provide initial safety data; however, the fundamental analysis begins post-marketing, when the drug is administered to diverse populations. Real-world evidence from patient experiences is continuously analyzed to detect emerging safety issues. This ongoing vigilance helps maintain a drug’s safety profile by evolving drug usage patterns.
-
Risk Communication & Mitigation
Pharmacovigilance plays a vital role in communicating risks to stakeholders, including healthcare providers, Regulatory authorities, and patients. Timely and proper communication ensures that everyone involved in the scenario can take necessary actions to manage potential harm caused by medication. Public Health advisories, updated package inserts, as well as direct communications with Healthcare providers are some of the standard methodologies used to propagate essential safety information.
A strong pharmacovigilance system helps in
- Detection of rare, serious, or even adverse reactions.
- Protection of the vulnerable population, such as children, the elderly, and pregnant women.
- Prevention of large-scale public health crises.
- Improvisation in rational drug and prescribing practices.
Lifecycle of a Drug Safety Program
Drug Safety Monitoring across the medicine lifecycle is a continuous process, and not a one-time process that is limited to approval. Each stage has a particular role in maintaining public health and patient safety.
- Pre-Clinical & Clinical Trials
Within the selected population, the initial safety signals are identified under controlled conditions. These trials help in the detection of common and short-term adverse effects, but cannot predict all real-world risks due to the limited testing population.
- Regulatory Approval
When the drug is known to outweigh the benefits over the risks, the regulatory board approves it, which shouldn’t be taken to mean it’s completely risk-free. Regulators, based on the available data, push the process further yet acknowledge the additional safety information that emerges post-approval.
- Early Post-Marketing Phase (Phase IV)
The monitoring intensifies once the drug is widely used. This runs across patients, irrespective of group, including those excluded from the trials. This aids in identifying rare, delayed, or population-specific adverse effects.
- Routine Pharmacovigilance
The collection and analysis of ADRs continuously help to track emerging safety trends. The signal detection ensures that the new risks are identified as prescribing patterns and changes in usage conditions.
- Risk Minimization & Regulatory Action
Upon confirmation of safety concerns through continuous evaluation, regulatory authorities may update the labels, restrict use, initiate further/ additional studies, or withdraw the drug. These measures make sure patient safety while preserving therapeutic benefits wherever possible without compromising.
How Adverse Events Are Detected and Analyzed
Multiple and complementary datasets are used to identify the adverse effects, ensuring that not a single safety signal is missed in real-world use.
- Spontaneous Reporting Systems (healthcare professionals & patients): As the name suggests, these systems capture unexpected or serious adverse reactions reported during routine clinical practice. This data often provides the first indication of evolving safety concerns.
- Clinical Studies and Post-authorization Safety Studies: Post-approval, additional studies are conducted within the specified populations that were not fully a part of the pre-approval trials. These studies help to identify long-term risks and evaluate rare reactions and safety.
- Electronic Health Records & Real-world Data: Large-scale healthcare databases serve as sources for understanding trends across millions of patients. This identifies the correlation between medicines and their adverse effects over time.
- Scientific Literature Monitoring: Regularly following newly reported safety findings in case studies and published works helps integrate additional information into safety assessments.
- Digital Health Tools and Wearables: Health data generated via mobile apps and wearable devices enables real-time detection (though it is not 100% accurate) of changes in physiological parameters that may signal ADRs.
Along with these strategies, advanced analytics such as statistical signal detection, AI-based data mining, and algorithm-based assessment are implemented to detect patterns that might have gone unnoticed in individual case reports.
Once the potential safety indication has been identified, it undergoes a well-structured evaluation process that includes
Medical evaluation → Benefit-risk analysis → Regulatory review → Further action if confirmed.
Pharmacovigilance Authorities and Regulatory Reporting Obligations
Various international and national Regulatory authorities monitor Pharmacovigilance activities. Some esteemed Regulatory authorities include:
- CDSCO: The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is responsible for Pharmacovigilance activities in India through its PvPI (Pharmacovigilance Programme of India) program.
- FDA: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) operates the MedWatch program as well as ensures compliance with the safety regulations.
- EMA: The European Medicines Agency (EMA) manages EudraVigilance for ADR reporting in the European Union regions.
- PDMA: Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) Oversees Pharmacovigilance in Japan region.
- WHO: The World Health Organization (WHO) maintains the global database of ADRs as well as promotes International harmonization of PV practices.
Pharmaceutical companies are legally obligated to submit:
- Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs)
- Periodic Safety Update Reports (PSURs/PBRERs)
- Risk Management Plans (RMPs)
Failure to comply can lead to penalties, product suspension, or market withdrawal.
Real World Case Studies Highlighting PV Impact
Thalidomide Tragedy
Post-marketing surveillance showed that thalidomide is linked to severe birth defects, which led to global regulatory reforms and modern PV systems.
Rofecoxib (Vioxx) Withdrawal
The drug was withdrawn from the market as the Pharmacovigilance data revealed increased cardiovascular risks. Following withdrawal, they focused on the improvement of the risk-benefit evaluation standards
COVID-19 Vaccines
Global PV systems rapidly detected rare adverse effects, such as myocarditis and thrombotic events, and updated labels in a timely manner, enabling patient safety while maintaining vaccination benefits.
Why Pharmacovigilance Matters Today
Pharmacovigilance is more crucial than ever, as it tracks the drug even after approval. They are critical due to
- Rapid drug approvals
- Complex biologics and gene therapies
- Polypharmacy in the aging population
- Global Medicine Access
A strong PV System helps in:
- Strengthening Public Trust
- Improving decision-making in healthcare
- Enabling safer innovation
- Ensuring accountability across the healthcare ecosystem
Break Into Pharmacovigilance – No Experience Needed!
Get 100% Placement Support + Work on LIVE PROJECTS
Speak to a PV Expert → https://btnk.org/contact-PV-Expert
Apply Now → https://btnk.org/PV-training-project
Pharmacovigilance is key to patients’ safety as well as public health. By identifying risks, taking decisive regulatory actions, as well as implementing safety protocols, Pharmacovigilance ensures that the drugs we use are effective, safe and free of harm or ADRs. As we move towards a future of Personalized Medicine as well as futuristic and advanced Therapeutics, the role of Pharmacovigilance will become more essential. We should stay vigilant, stay informed, as well as support the efforts of Pharmacovigilance—because drug safety is a responsibility we all share.